Monday, November 2, 2020, significant 20 years given that the very first team resided on the International Space Station. Since then the football field-sized task of engineering has actually hosted 26 European objectives and supported over 2700 global experiments to enhance life on Earth and in area. Credit: ESA/NASA
As the world commemorates 20 years of people in orbit around Earth on the International Space Station, this month’s science summary will recall not at 4 weeks of European research study in area, however 20 years – with a concentrate on human research study, naturally.
In November 2000 the very first human went into the two-module International Space Station and ESA ran its very first experiment simply 3 months later on.
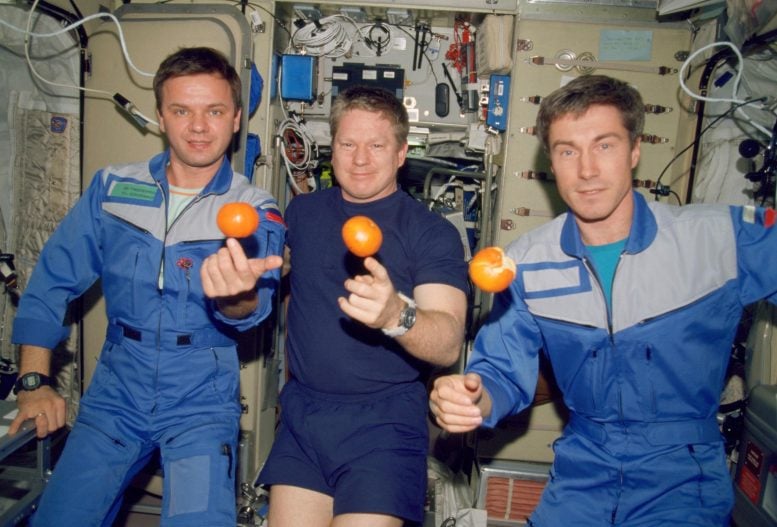

Expedition 1 team in December 2000 ready to consume oranges in the Zvezda module of the International Space Station. From left cosmonaut Yuri Gidzenko NASA astronaut William Shepherd and cosmonaut Sergei Krikalev. Expedition 1 was the very first team to survive on the International Space Station. Credit: NASA
ESA’s human spaceflight research study organizer Jennifer Ngo-Anh describes the advantages of Space Station research study, “We typically run three types of experiments, research that cannot be done on Earth, research to understand and improve astronaut health and research that exploits the unique aspect of sending perfectly healthy and fit humans into a new and stressful environment.”
“As you will see from the list below, this research is helping us explore farther into our Solar System, but it benefits people on Earth with new knowledge, new technology, and new techniques – spaceflight is a motor for ingenuity.”

This infographic reveals a few of the advantages for mankind that have actually been provided through ESA’s human and robotic spaceflight program. The difficulties of area expedition speed up development for all on Earth. Human and robotic spaceflight is moving innovation towards a circular economy by enhancing effectiveness in energy, automation, robotics, expert system, habitation innovation, recycling, waste management, and additive production. Credit: ESA–K. Oldenberg
Here are 20 of ESA’s preferred experiments from 20 years of habitation:
- Brain-DTI
This research study took brain scans of astronauts to determine ‘plasticity’ or how rapidly their brains adjust to brand-new inputs. The comforting conclusion is that brains adjust remarkably well, though research study is hinting that the results of drifting in weightlessness mark the brain permanently.
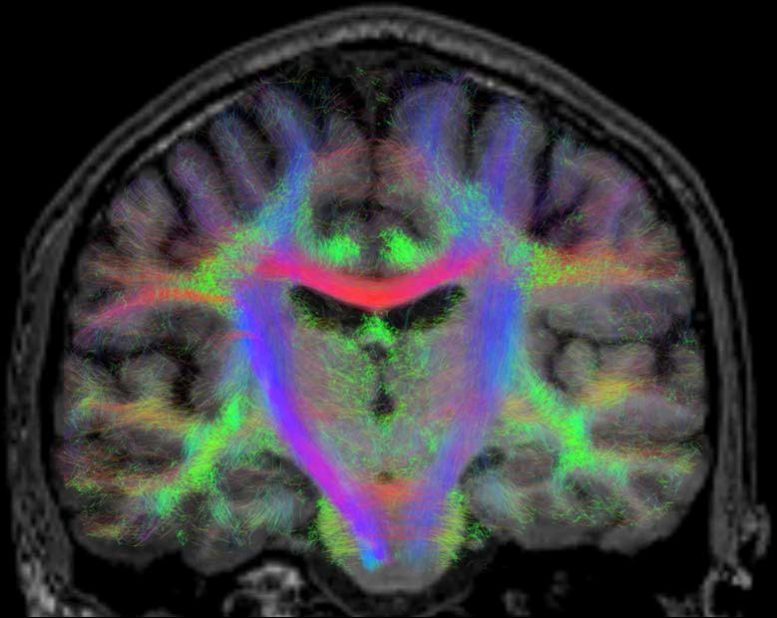
An MRI scan of a volunteer’s brain for the BRAIN-DTI experiment utilizing tractography to reveal neural networks. Credit: B. Jeurissen
- 42 is the response
The Biolab center in Columbus was utilized to examine the time it considers mammal immune cells to adjust to microgravity: 42 seconds, coincidentally the significance of life according to Douglas Adams in The Hitchhiker’s Guide to the Galaxy and the variety of the Space Station Expedition that carried out the experiment! - Circadian Rhythms
This experiment keeps track of an astronaut’s body temperature level to learn more about our biological rhythm. An unique non-invasive thermometer was developed and marketed on Earth to get outcomes that surprised scientists as it revealed a continual boost in body temperature level. - Endothelial cells
Research into the cells that line our capillary is assisting comprehend how and why they agreement and broaden, and why they have actually lowered performance in aging on Earth.
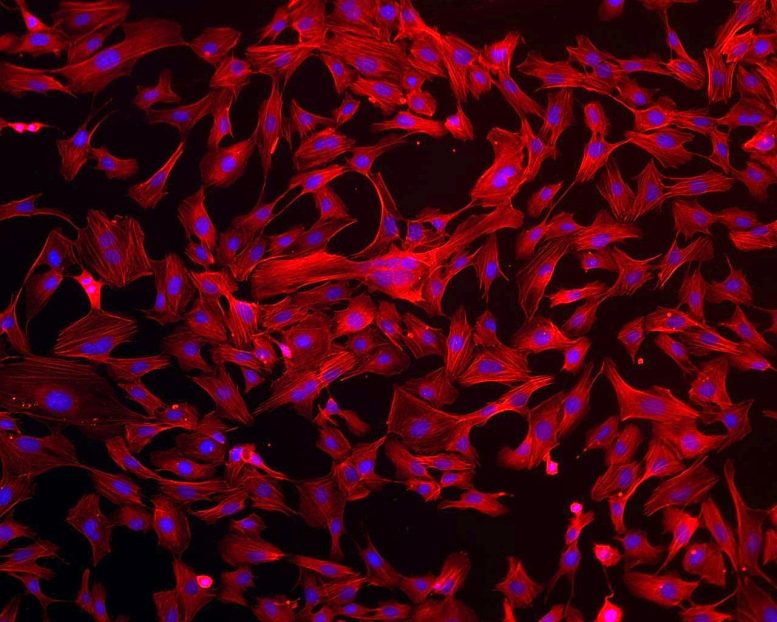
Components of human endothelial cells stained for recognition. In red is the ‘actin’ protein that enables the cells to move, adhere, divide, and respond to stimuli. In blue are the cell nuclei consisting of DNA. Credit: Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna, Pisa, Italy
- Growing capillary
Not material with simply observing capillary, how about growing brand-new ones in area? This experiment made use of weightlessness to see if we can grow brand-new three-dimensional organs. On Earth, gravity pulls the cells down making 3D-structures more difficult to accomplish in the laboratory. - Better sleep
Sleep is very important, and looking out much more so if you will dock 2 spacecraft lots of countless kilometers far from Earth. But how do you make sure astronauts get an excellent night sleep when the Sun sets 16 times a day seen from the International Space Station? Structure, light and chemical help if essential is the response (up until now), and these findings use to you on Earth too. - Vessel-ID
This experiment is not research study into people, however it did actually conserve lives. The Vessel-ID worldwide traffic tracking receiver was checked outside the Columbus lab and got a distress beacon from a fishing ship; search and rescue authorities were then informed. What we gained from this experiment is now flying as a stand-alone satellite. - Stressed body immune systems
The Immuno experiment took a holistic technique to examining tension by making use of surveys, blood samples and temperature level readings from the astronauts revealing that the body immune system goes crazy. Through need, scientists established brand-new methods of examining little amounts of blood, so as not to drain pipes the astronauts’ already-depleted materials. Now, the hardware and the techniques utilized are being shown the medical neighborhood to help the care of at-risk new-borns, who have even less blood to spare for analysis. - Osteoporosis – salt ain’t great
Astronaut bones go through sped up osteoporosis throughout spaceflight. This illness expenses Europe around €25 billion a year and usually impacts the senior, leading to fragile and vulnerable bones and damaged hips and arms from falls. Studying astronauts in area revealed that level of acidity in the body speeds up bone loss, and you can combat the level of acidity by consuming less salt or taking bicarbonate tablets as an easy preventive step. On Earth a research study would take years to see outcomes, however the sped up aging seen in astronauts enables scientists to fast-track concepts.
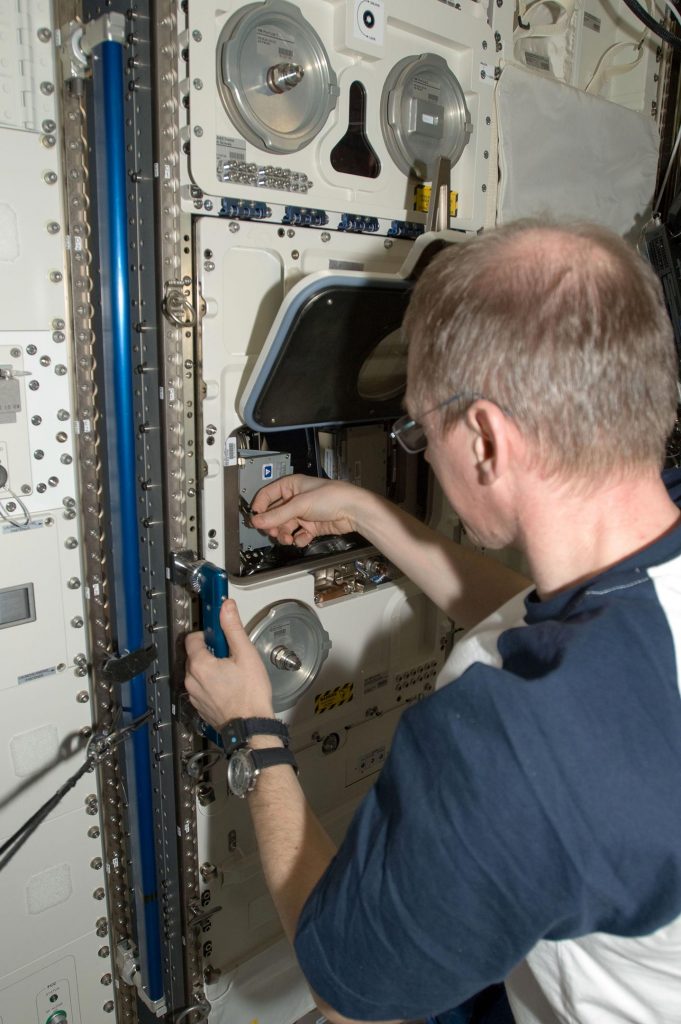

ESA astronaut Frank De Winne sets up experiment containers for the Yeast experiment in the Biolab incubator in Columbus on October 2, 2009. Credit: NASA
- 3D bone scanner
To act on the above research study in more information, the EDOS-1 and 2 experiments needed much better medical scanners to see the finer structure of astronaut bones – so they developed simply that. The Xtreme CT scanner ESA assisted establish can reveal the tiny architecture of bones and their strength to keep an eye on bones of everybody on and around Earth. - Yeast
Another experiment in Biolab examined yeast stress that have actually been utilized to make bread and brew beverages for centuries. Unsurprisingly, in microgravity the yeast revealed indications of tension and had issues developing cell walls. The cells diverted their energy to fix themselves and grew less rapidly. By examining the stress that carried out much better in microgravity, scientists might recognize genes that might be utilized for longer area objectives. Space-faring yeasts can be cultured for future objectives to far-away worlds – area pastry shop anybody?
- 5-LOX
The 5-LOX enzyme controls life span of human cells. Most human cells divide and restore, however the variety of times they reproduce is restricted. Italian scientists wished to discover how this enzyme was impacting astronauts’ health in area and discovered that cells flown in area revealed more 5-LOX activity than the centrifuged samples, offering researchers a target enzyme that might contribute in the weakening of body immune systems. The enzyme can be obstructed with existing drugs, so utilizing these findings to enhance human health is a close truth. Who understands what life-prolonging tablets might be established in the future, all thanks to a two-day area experiment. - Finding the secret
A comparable experiment put immune cells through synthetic gravity in area and revealed that a particular transmitter in the cells, called the Rel/NF-kB path, quits working in weightlessness. Finding which gene does what resembles trying to find the ideal secret to fit a keyhole, without having actually discovered the keyhole yet. Studying cells that have actually flown on the International Space Station is putting scientists on the ideal course to discovering the secret to how our body immune system works. The pharmaceutical market might likewise discover the genes that require to be active to eliminate particular health problems and market customized antibodies. - Laser eyes
Where do astronauts search in area? An easy concern for science, however to address it the research study group behind this experiment required to track the astronauts’ eyes at all times. New hardware was established for this area research study and it is now discovered in nearly all laser-eye surgical treatments in Europe where surgical accuracy is essential.
Cosmonaut Sergei Krikalev using ESA’s Eye Tracking Device throughout Expedition 11 to the International Space Station in 2005. Credit: ESA/NASA
- Remote medical diagnosis
Keeping an astronaut healthy and fit from a range is the flight cosmetic surgeon’s job on Earth. Not all astronauts can be medical physicians, so little, user friendly makers are needed for medical diagnosis however likewise for research study into human health. Great strides have actually been made over the last 20 years in ultrasound makers, heart-rate displays, thermometers in addition to in operating and sending out the information to doctor lots of countless kilometers away. The Tempus Pro device is the conclusion of this and can be utilized similarly efficiently all over our world. - Stay strong
Strong muscles are effort on Earth – and even harder in area where particular muscles utilized to stroll or sit are not required in weightlessness, the “antigravity muscles”. Studies have actually revealed that astronauts experience approximately a 20% loss of muscle mass in short-duration objectives alone, which is stressing for an astronaut ready to arrive on Mars after a nine-month flight. The Muscle Biopsy experiment is examining how cells interact (called signaling paths). Researchers suspect cell interaction is connected to gravity-sensing which the cells interact less in area. The research study is still in development however the science group currently have images from muscle biopsies that reveal bigger intramuscular tissue areas after a flight, a preliminary verification of their hypothesis. - Lung health
How do lungs adjust to spaceflight? This Swedish-led research study put astronauts in the Space Station’s airlock and drained air to decrease the pressure, revealing unexpected lead to the nitric oxide levels breathed out. Researchers established a drug with a uniquely selective result in lung flow. The drug expands the capillary and combats deadly boosts of regional high blood pressure. On the Moon and Mars, astronauts’ lungs might end up being quickly inflamed or irritated by dust particles as they don’t settle to the ground however distribute constantly.
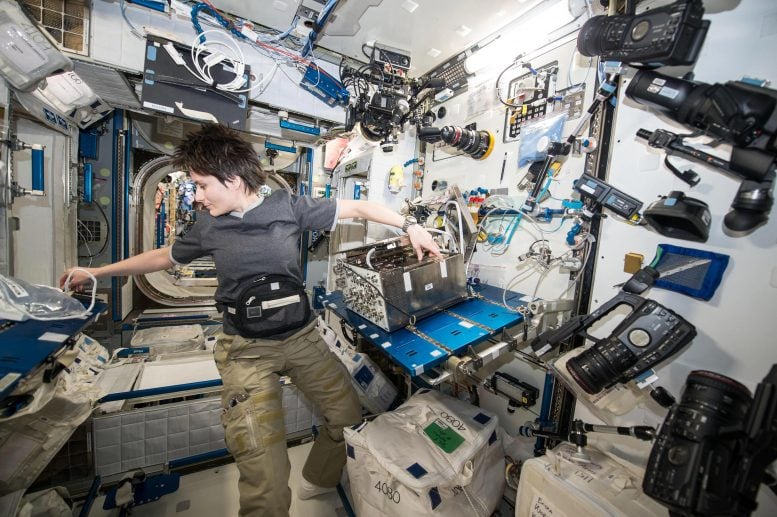

ESA astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti on the International Space Station dealing with devices for the Airway Monitoring examination. Credit: ESA/NASA
- Old age
Our brains alter all the time – nerves and linking cells reorganize to every brand-new experience, however end up being less proficient at it in aging. Scientists peered inside astronauts’ heads for the Neurospat experiment to comprehend how they adjust to their brand-new environments and established brand-new tools for screening spatial cognition that will be of fantastic assistance to our aging brains. - Humans are cleaner than we believed
For twenty years people have actually been residing in the closed International Space Station – without a shower to clean in. There is no put on Earth where scientists can examine how germs develop and reside in such a tight-knit environment. Concern about widespread germs development is constantly here, however it ends up that it is not that bad, with around 55 kinds of germs discovering healthy balance around the Space Station. This doesn’t imply that research study is being done into easy-clean products that will keep germs in check. - Mix it up
This series of experiments is physics-based, however taking a look at how liquids blend on a molecular level is enhancing shelf-life of medication on Earth. The SODI experiments in essence observe 2 liquids together in weightlessness. As the 2 liquids continuously socialize and disrupt each other, the outcomes are fascinating for business establishing anti-body-based medication that is infamously understood to be unsteady liquids.
This is simply a little choice of the European experiments operate on the International Space Station that concentrate on human research study. Around 400 ESA examinations have actually been carried out given that the very first module was released and thousands more are led by the 4 other area companies that interact to keep the Space Station up: NASA, Russia’s Roscosmos, Japan’s JAXA, and the Canadian Space Agency.
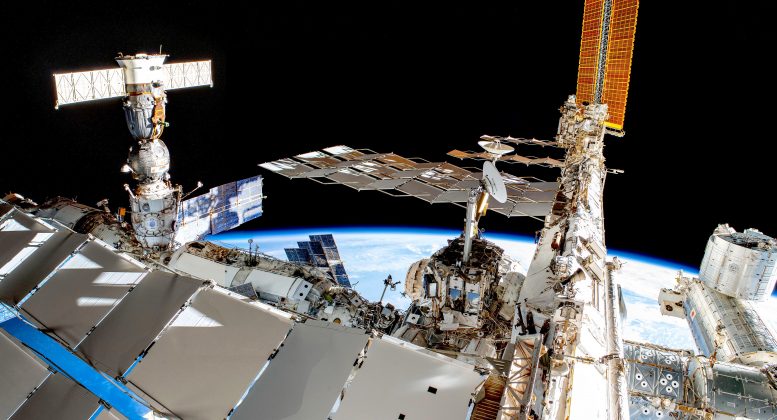

This panorama of the International Space Station is a larger view of what ESA astronaut Luca Parmitano was catching on cam throughout the very first of a series of historical spacewalks that happened in November 2019. Author, reporter and scientist Lee Brandon-Cremer developed this image by sewing together 3 images taken by Luca as he made his method to the worksite throughout the very first Extravehicular Activity or EVA to service the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS), the Station’s dark matter detector. Credit: L. Brandon-Cremer
With the Space Station set to continue running for a lot more years, the future is brilliant for research study in our special lab. “We listened to researchers and companies and are making space research more accessible, for example with companies offering services to design, build, fly and run experiments in one package deal,” states Jennifer.
“Research run on the Space Station almost always delivers surprising results, advancing our knowledge of the world, humankind and benefiting people on Earth. For 20 years we have been working on the forefront of where science and engineering meet, and I am looking forward to seeing many more years of interesting experiments and results.”





