A current research study led byDr Wei andDr Qiao from the First Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources offers an assessment of the efficiency of the recently launched CMIP6 designs in mimicing the worldwide warming downturn observed in the early 2000 s. This research study exposes that the type in mimicing and anticipating near-term temperate modification is to properly separate and replicate the 2 unique signals, i.e., the human-induced long-lasting warming pattern and natural irregularities, particularly those at interannual, interdecadal, and multidecadal scales. This work was online released in Science China Earth Sciences
After the unmatched warming over the last quarter of the 20 th century, the worldwide surface area temperature level development slowed all of a sudden throughout 1998-2013 regardless of the sharp boost in greenhouse gas emissions; this phenomenon is called the worldwide warming hiatus or downturn to be more accurate. The worldwide warming downturn challenges the existing clinical understanding of worldwide temperature level modification systems, therefore has actually been among the most worrying concerns in current environment research study and even public.
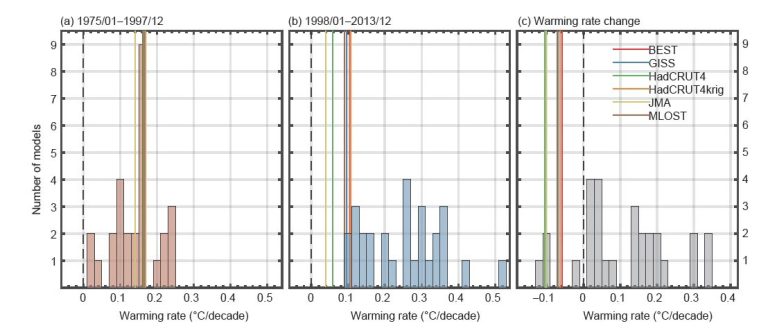
Figure 1. Warming rates throughout the quick warming duration (1975/01-1997/12) (a) and the warming hiatus duration (1998/01-2013/12) (b) and the warming rate modification throughout the hiatus duration relative to the quick warming duration (c). All warming rates are originated from the 28 simulated (bars) and 6 observed (vertical lines) worldwide temperature level time series. Credit: ©Science China Press
However, the advanced and innovative environment designs in CMIP5 might not replicate this warming downturn. During 1998-2013, the designs primarily provide a quickly warming rise which significantly differs the observed flat temperature level time series. The designs substantially overstate the observed warming rate of the current duration. IPCC AR5 mentioned:“Almost all CMIP5 historical simulations do not reproduce the observed recent warming hiatus” Therefore, the simulation and forecast capability of advanced environment designs have actually been questioned.
Now the CMIP6 design information are slowly launched given that2020 The recently established designs consist of much better understanding of the worldwide temperature level modification systems, particularly more affordable physical procedures of natural irregularities. Successful simulations of the worldwide warming downturn are anticipated in the new-generation designs. As the information of 28 brand-new designs appear, it is essential to prompt take a look at the capability of the CMIP6 designs on providing the current warming downturn.
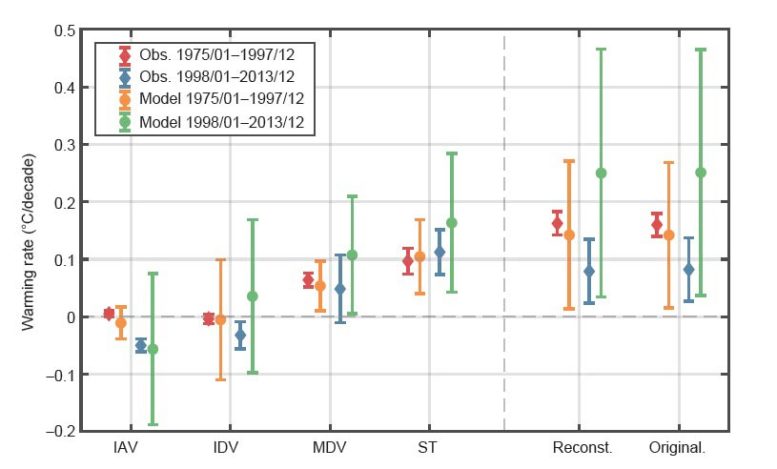
Figure 2. Warming rates of interannual, interdecadal, and multidecadal irregularities (IAV, IDV, MDV) and the nonreligious pattern (ST) throughout the quick warming duration (1975/01-1997/12, left signs) and the warming hiatus duration (1998/01-2013/12, ideal signs) originated from the 28 simulated (orange and green pentagrams) and 6 observed (red and blue bars) worldwide temperature level time series. Credit: ©Science China Press
By contrast to 6 commonly utilized worldwide surface area temperature level datasets, research study group from First Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources examines the efficiency of the 28 recently launched CMIP6 designs in mimicing the current warming downturn, and discovers that a lot of CMIP6 designs still stop working to recreate the warming downturn, although they provide some motivating enhancements when compared to CMIP5 designs (Figure 1).
Further, they checked out the possible factors for the trouble of CMIP6 designs in mimicing the current warming downturn. They expose that it is related to the designs’ shortages in mimicing the unique temperature level modification signals from the human-induced long-lasting warming pattern and/or the 3 vital natural irregularities at interannual, interdecadal, and multidecadal scales (Figure 2).
This research study exposes that the type in mimicing and anticipating near-term temperate modification is to properly separate and replicate the 2 unique signals, i.e., the human-induced long-lasting warming pattern and natural irregularities, particularly those at interannual, interdecadal and multidecadal scales. This recommends that the key-scale irregularities need more attention in the designs, considering their important functions in regulating the warming rate modification at decadal to multidecadal scales. This result can supply crucial insight for the simulation and forecast of near-term environment modifications.
Reference: “Could CMIP6 climate models reproduce the early-2000s global warming slowdown?” by Meng Wei, Qi Shu, Zhenya Song, Yajuan Song, Xiaodan Yang, Yongqing Guo, Xinfang Li and Fangli Qiao, 15 April 2021, Science China Earth Sciences
DOI: 10.1007/ s11430-020-9740 -3
This research study was moneyed by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos 41806043 & & 41821004).





