Hera utilizes infrared to scan effect crater. Credit: ESA – ScienceOffice.org
Today ESA granted a €129.4 million (United States $153.4 million) agreement covering the in-depth style, production, and screening of Hera, the Agency’s very first objective for planetary defense. This enthusiastic objective will be Europe’s contribution to a global asteroid deflection effort, set to carry out continual expedition of a double asteroid system.
Hera – called after the Greek goddess of marital relationship – will be, together with NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirect Test (DART) spacecraft, mankind’s very first probe to rendezvous with a binary asteroid system, a little understood class comprising around 15% of all understood asteroids.
The agreement was signed today by Franco Ongaro, ESA Director of Technology, Engineering and Quality, and Marco Fuchs, CEO of Germany area business OHB, prime specialist of the Hera consortium. The finalizing occurred at ESA’s ESOC center in Germany, which will work as objective control for the 2024-introduced Hera.
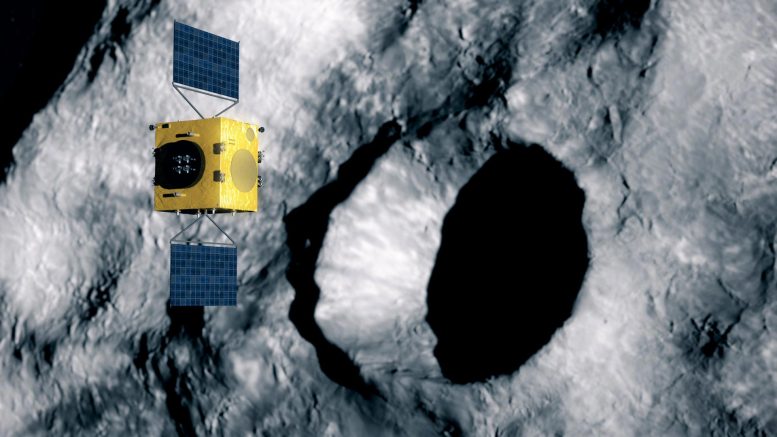

Hera scans DART’s effect crater. Credit: ESA – Science Office
Hera is the European contribution to a global planetary defense partnership amongst European and United States researchers called the Asteroid Impact & Deflection Assessment, AIDA. The DART spacecraft – due for launch in July 2021 – will initially carry out a kinetic effect on the smaller sized of the 2 bodies. Hera will follow-up with an in-depth post-impact study to turn this grand-scale experiment into a well-understood and repeatable asteroid deflection strategy.
While doing so, the desk-sized Hera will likewise show several unique innovations, such as self-governing navigation around the asteroid – like modern-day driverless cars and trucks on Earth – while collecting important clinical information, to assist researchers and future objective organizers much better comprehend asteroid structures and structures.

NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirect Test, DART, objective is planned to hit the smaller sized of 2 bodies of the Didymos binary asteroid system in fall 2022. ESA’s Hera objective will then carry out follow-up post-impact observations. Credit: ESA
Hera will likewise release Europe’s very first ‘CubeSats’ (mini satellites developed from 10 cm boxes) into deep area for close-up asteroid surveying, consisting of the extremely first radar probe of an asteroid’s interior – utilizing an upgraded variation of the radar system continued ESA’s Rosetta comet objective.
Due to release in October 2024, Hera will take a trip to a binary asteroid system – the Didymos set of near-Earth asteroids. The 780 m-diameter mountain-sized primary body is orbited by a 160 m moon, officially christened ‘Dimorphos’ in June 2020, about the exact same size as the Great Pyramid of Giza.
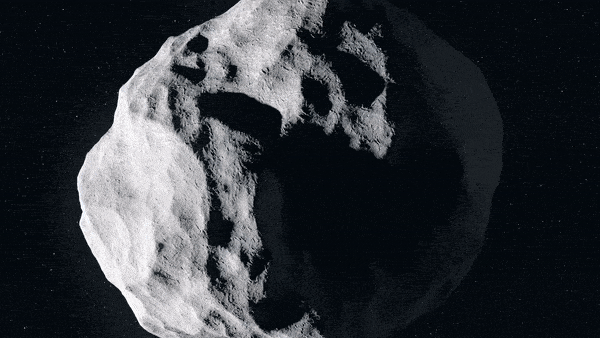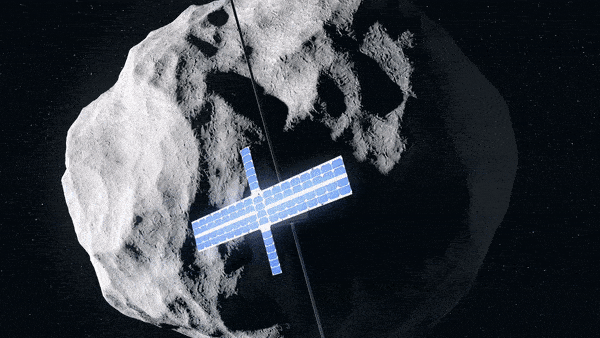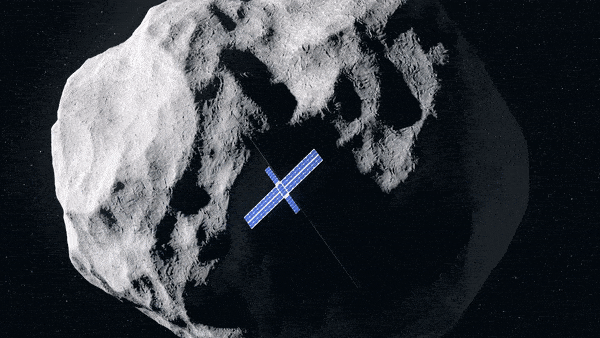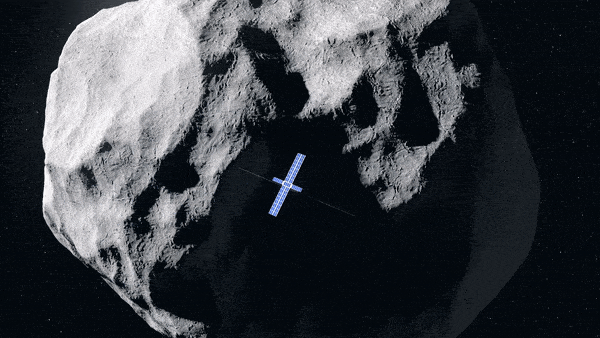
Hera’s Juventas CubeSat coming in for landing on the smaller sized Didymos asteroid. Credit: ESA-Science Office
DART’s kinetic effect into Dimorphos in September 2022 is anticipated to change its orbit around Didymos in addition to develop a considerable crater. This moonlet asteroid will end up being distinct, as the very first heavenly body to have its orbital and physical qualities deliberately modified by human intervention. Hera will get to the Didymos system at the end of 2026, to carry out a minimum of 6 months of close-up research study.
Hera’s objective control will be based at ESA’s ESOC center in Darmstadt, Germany, likewise the house of ESA’s brand-new Space Safety and Security program, of which Hera belongs.
This agreement finalizing covers the complete Hera satellite advancement, combination and test, including its innovative assistance, navigation and control (GNC) system. Contracts for Hera’s 2 hosted CubeSats and appropriate innovation advancements are currently continuous.
Hera’s European partners
The agreement has actually been granted to a consortium led by prime specialist OHB System AG in Bremen.
Of 17 ESA Member States adding to Hera, Germany remains in the leading edge, entrusted with the total Hera spacecraft style and combination, primary navigation cams, tanks, thrusters, high-gain antenna, response wheels, and mass memory system.
Italy is leading the objective’s power and propulsion subsystems, and is offering the deep-space transponder that will allow the objective’s radioscience experiment. In addition, Italy is leading the dust and mineral prospecting CubeSat, called after the late Andrea Milani, recognized teacher and leading asteroid researcher.
Belgium is establishing Hera’s on-board computer system and software application, the brain of the spacecraft, plus its power conditioning and circulation system – the heart of its electrical subsystem. It is likewise adding to Hera’s Japanese-established thermal imager and CubeSats operations center at ESA/ESEC.
Luxembourg is leading the radar-hosting ‘Juventas’ CubeSat and the inter-satellite interaction system permitting the 2 Hera CubeSats to interact with Earth through an ingenious network utilizing Hera as information relay.
Portugal and Romania are establishing the laser altimeter which will supply important info for the self-governing navigation functions. In addition, Romania is establishing the image processing system, harness and the electrical test devices (while likewise adding to its GNC advancement).
The Czech Republic is accountable for the complete satellite structure, payload software application (to command the instruments), independent software application recognition and ground assistance devices for pre-flight satellite screening. It is likewise offering parts for Juventas’ low-frequency radar and information processing software application on the 2nd CubeSat.
And Spain is establishing Hera’s innovative assistance, navigation and control system in addition to the deep-space interaction system. It is likewise offering the Juventas gravimeter instrument.
- Austria is supporting with objective information analysis and processing
- Denmark is adding to the Juventas CubeSat and remote terminal system
- France is offering Juventas’ low-frequency radar, in addition to star trackers and assistance to the CubeSats’ payload operations preparing and close-proximity trajectories
- Hungary is supporting clinical calibration of the cams
- The Netherlands is establishing the brand-new deep-space CubeSat release system and offering Hera’s Sun sensing units
- Switzerland is contributing with structural components and systems for the solar ranges
- Finland is offering the 2nd CubeSats’ multi-spectral imager and onboard devices. It is likewise offering the information processing system
- Poland is contributing with Juventas’ low-frequency radar deployable antennas
- Ireland is offering an ingenious inertial measurement system for the Hera spacecraft to support deep-space navigation
- ESA Associate Member State Latvia is contributing a time-of-flight detector for the objective’s laser altimeter.





