Researchers from the Hubrecht Institute mapped the restoration of the center after a coronary heart assault with nice element. They discovered that coronary heart muscle cells — additionally referred to as cardiomyocytes — play an essential function within the intracellular communication after a coronary heart assault. The researchers documented their findings in a database that’s accessible for scientists world wide. This brings the analysis area a step nearer to the event of therapies for improved restoration after coronary heart harm. The outcomes have been revealed in Communications Biology on the 29th of January.
In the Netherlands, a mean of 95 individuals find yourself within the hospital every day due to a coronary heart assault. During a coronary heart assault, the blood provide to part of the center is blocked, for instance resulting from a blood clot in a coronary artery. Attempts to revive the blood provide are made as quickly as doable, also called reperfusion. However, part of the center has already been with out oxygen for a while. Depending on the dimensions and period of the infarction, this causes coronary heart muscle cells — additionally referred to as cardiomyocytes — to die. This can lead to the formation of scar tissue, which is stiffer than regular coronary heart tissue and subsequently makes it tougher for the center to correctly contract. This may cause the pumping perform of the center to deteriorate, which might ultimately result in coronary heart failure.
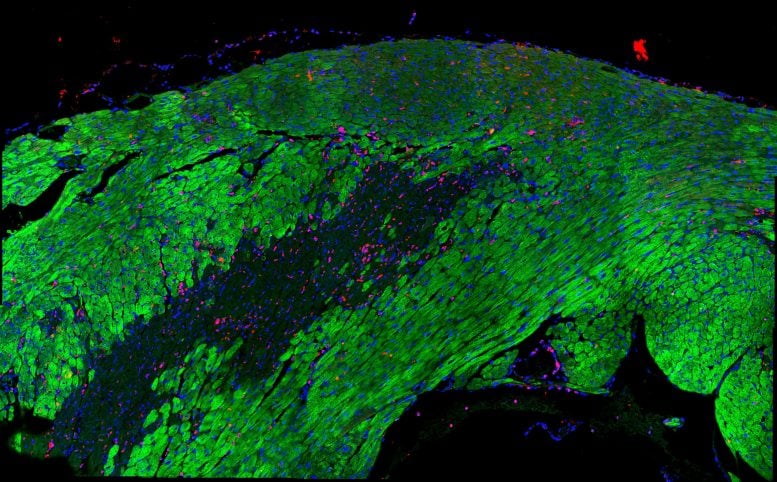
Shown is an infarcted coronary heart during which inexperienced represents cardiomyocytes (coronary heart muscle cells), crimson exhibits B2M expression and blue represents cell nuclei. The space disadvantaged of inexperienced is the infarcted space. Credit: Louk Timmer © Hubrecht Institute
Heart restoration
In different phrases, perception into the restoration of the center after a coronary heart assault and the way this results in the formation of scar tissue is extraordinarily essential. However, a lot continues to be unknown. Reason sufficient for researchers from the lab of Eva van Rooij to look at this additional. They studied how the hearts of mice recuperate at three totally different time factors following a coronary heart assault. To this finish, they used single cell sequencing, a way that allows the examination of the RNA of particular person cells. The researchers generated an unlimited dataset with details about the function of several types of cells through the restoration course of after a coronary heart assault.
Communication community
Consequently, they used the information to map a communication community. Louk Timmer, researcher on the undertaking, explains: “Cells communicate with each other by secreting molecules. These molecules then trigger the recipient cell to take a specific action, which may be important for the recovery process. We have now mapped with great detail how different cells communicate with each other at different time points after a heart attack. That had never been done so thoroughly before.” This communication community is now documented in a database and accessible to scientists world wide.
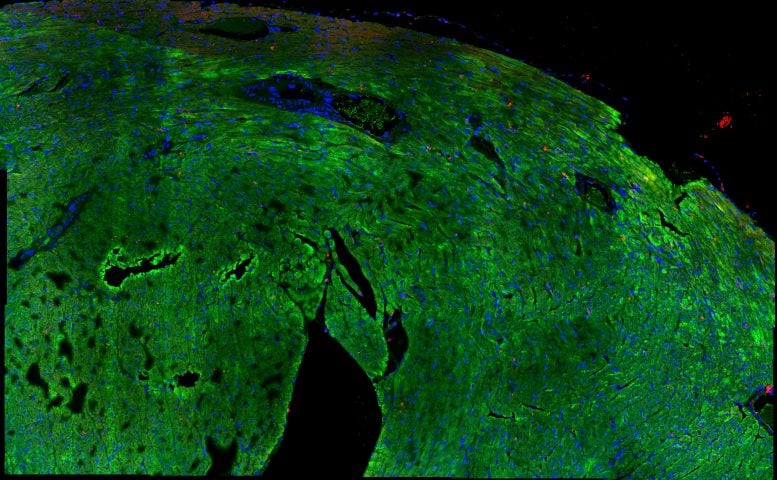
Shown is a management coronary heart during which inexperienced represents cardiomyocytes (coronary heart muscle cells), crimson exhibits B2M expression and blue represents cell nuclei. Credit: Louk Timmer © Hubrecht Institute
Formation of scar tissue
Especially the function of cardiomyocytes within the restoration following a coronary heart assault was nonetheless largely unknown, partly due to technical difficulties. However, one other current paper from Van Rooij’s lab solved these obstacles, permitting the researchers to particularly examine the perform of cardiomyocytes within the restoration course of. “We noticed that at the earliest time point measured after the heart attack, cardiomyocytes were secreting increased amounts of a molecule called B2M. Subsequent experiments showed that the secretion of B2M can result in the activation of so-called fibroblasts — cells responsible for the formation of scar tissue,” says Timmer. Cardiomyocytes thus appear to not directly stimulate the manufacturing of scar tissue early within the restoration course of. “Intuitively, we already thought that cardiomyocytes play an important role in intracellular communication during heart recovery and it is great that we have now been able to confirm that.”
Improve restoration course of
When requested in regards to the subsequent steps inside this area of analysis, Timmer emphasizes the significance of extra research. “Various scientists and experts can use this data, which enables us to gain a better understanding of the cells and molecules that are involved in the recovery of the heart and the way they communicate with each other. Hopefully, we can eventually improve the recovery process, so that people end up with less damage after a heart attack.”
Reference: “Single-cell transcriptomics following ischemic injury identifies a role for B2M in cardiac repair” by Bas Molenaar, Louk T. Timmer, Marjolein Droog, Ilaria Perini, Danielle Versteeg, Lieneke Kooijman, Jantine Monshouwer-Kloots, Hesther de Ruiter, Monika M. Gladka and Eva van Rooij, 29 January 2021, Communications Biology.
DOI: 10.1038/s42003-020-01636-3
Eva van Rooij is group chief on the Hubrecht Institute and professor of Molecular Cardiology on the University Medical Center Utrecht.





