Mice fed high-fat diet plan and supplement abundant in calcium, magnesium didn’t establish liver cancer.
Results from a preclinical research study include brand-new proof that a multi-mineral dietary supplement referred to as Aquamin might be a basic and efficient method to minimize the long-lasting health repercussions of non-alcoholic fatty liver illness. Aquamin, which is originated from calcified red marine algae, is abundant in calcium, magnesium, and 72 other minerals and micronutrient.
About 25% of individuals in the U.S are impacted by non-alcoholic fatty liver illness, which is defined by an excess of fat saved in the liver. Some individuals with this illness establish a more aggressive type referred to as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in which the liver is swollen. This can advance to fibrosis, advanced scarring referred to as cirrhosis, liver failure, and cancer.
“Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is a growing public health challenge that is currently being addressed through an emphasis on lifestyle changes, especially diet, to prevent fat build-up in the liver,” stated research study group leader Muhammad Nadeem Aslam, MD, from the University of Michigan in AnnArbor “New approaches are needed because this doesn’t work for everyone.”
Isabelle Harber, an undergraduate scientist in Aslam’s laboratory, will provide the brand-new research study at the American Society for Investigative Pathology yearly conference throughout the Experimental Biology (EB) 2022 conference, to be held April 2– 5 in Philadelphia.
“Most people living in Western society do not meet the USDA daily intake guidelines for the intake of calcium and magnesium and, presumably, other minerals nutritionally associated with these minerals,” statedHarber “We are working to find out if a mineral supplement could provide a low-cost, low- to no-toxicity approach to mitigating the devastated consequences of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.”
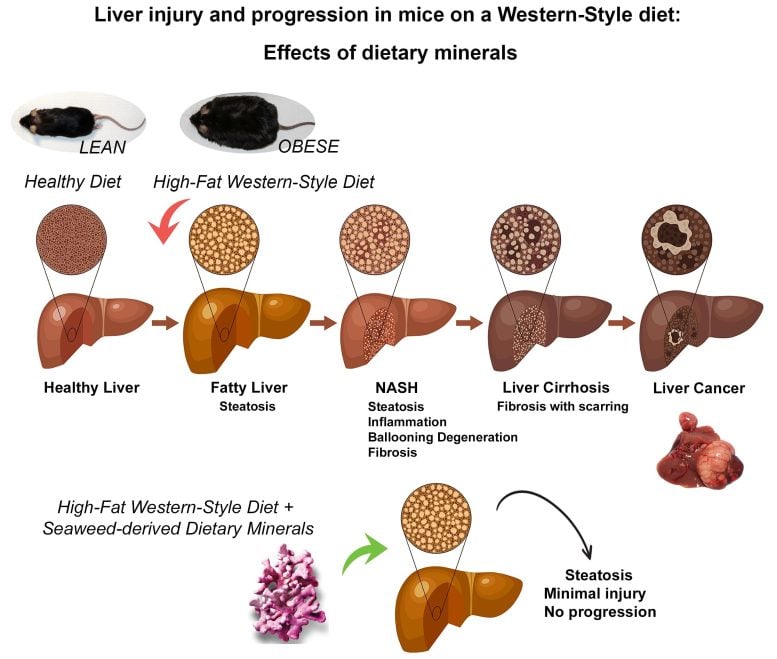
Overindulgence of dietary fats and carbohydrates causes weight problems and associated metabolic conditions consisting of fatty liver illness. Some individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver illness establish a more aggressive type referred to as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in which the liver is swollen. This can advance to sophisticated scarring referred to as cirrhosis, which can result in liver failure and cancer. However, Aquamin, which is abundant in calcium, magnesium and extra components (originated from calcified red algae), might assist stop this development. Credit: Aslam MN, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor
In initial research studies, the scientists fed mice a high-fat diet plan to cause the advancement of non-alcoholic fatty liver illness and NASH. They studied these mice for 15 to 18 months to observe the complete spectrum of liver illness, consisting of sophisticated fibrotic modifications and liver cancer.
These research studies exposed a remarkable decrease in late-stage repercussions of NASH in the animals that were fed the high-fat diet plan and got the multi-mineral supplement, compared to those that didn’t get the supplement. In short-term research studies lasting about 24 weeks, the scientists determined protein modifications connected with the NASH and minimized growth development in the longer research studies.
“In the long-term studies, we observed that most of the mice on the high-fat diet had large liver tumors while the mice on the same diet had no tumors when they received the mineral supplement,” statedAslam “These results confirmed our earlier findings that minerals may have the potential to reduce the downstream consequences of fatty liver disease.”
Because the brief- and long-lasting research studies were carried out utilizing various kinds of mice, the scientists next strategy to carry out both sets of research studies in the exact same animals. This will enable them to determine early protein modifications in private animals that might anticipate later on repercussions or be connected with defense from such repercussions.
They just recently finished a 90- day pilot stage trial in 30 healthy clients at threat for colorectal cancer who were randomized to get Aquamin or a placebo. The trial revealed that the mineral supplement didn’t present any security or tolerability problems, consisting of any prospective liver damage. They are likewise beginning to carry out pilot scientific research studies to examine Aquamin for security and tolerability for 180 days. Liver injury and swelling markers will belong to the research study endpoints.
Isabelle Harber will provide this research study from 11: 45 a.m.–12: 45 p.m., Sunday, April 3, in Exhibit/Poster Hall A-B, Pennsylvania Convention Center (Poster Board Number D20) ( abstract) and 6 p.m., April 3, in Terrace 2/3 ( abstract). Contact the media group for additional information or to acquire a complimentary press pass to go to the conference.
Meeting: Experimental Biology 2022





