If a satellite is damaged, the particles fans out in orbit and presents severe dangers to other satellites or crewed spacecraft. Credit: ESA/ID&&Sense/ ONiRiXEL
On November 15, 2021, U.S. authorities revealed that they had actually spotted a hazardous brand-new particles field in orbit nearEarth Later in the day, it was verified that Russia had actually damaged among its old satellites in a test of an anti-satellite weapon. Wendy Whitman Cobb is an area security scientist. She discusses what these weapons are and why the particles they develop is an issue now– and in the future.
What do we understand?
Russia released an anti-satellite test that damaged among its older satellites. The satellite separated and developed countless pieces of particles in orbit, varying in size from small specks as much as pieces a couple of feet throughout. This area scrap will stick around in orbit for several years, possibly hitting other satellites along with the International SpaceStation The spaceport station team has actually currently needed to shelter in location as they passed near the particles cloud.

Many anti-satellite weapons are rockets released from the ground, like this U.S. ASM-135 ASAT. Credit: Lorax
What’s an anti-satellite weapon?
Anti- satellite weapons, frequently described as ASATs, are any weapon that can momentarily hinder or completely damage an orbiting satellite. The one that Russia simply checked is referred to as a direct climb kinetic anti-satellite weapon. These are generally released from the ground or from the wings of an aircraft and damage satellites by encountering them at high speeds.
A comparable weapon type, called co-orbital anti-satellite weapons, are very first released into orbit and after that alter instructions to hit the targeted satellite from area.
A 3rd type, non-kinetic anti-satellite weapons, utilize innovation like lasers to interrupt satellites without physically hitting them.
Space firms have actually been establishing and evaluating anti-satellite weapons because the 1960 s. To date, the U.S., Russia, China, and India have actually shown the capability to attack satellites in orbit that support services like GPS, interactions, and weather condition forecasting.
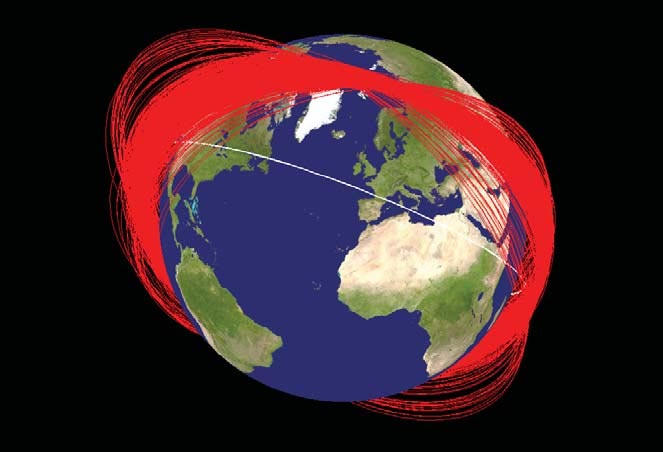
Debris from a single damaged satellite can expand quickly, as seen in this image revealing the orbits of particles from a Chinese satellite one month after it was damaged in2007 Credit: NASA Orbital Debris Program Office
Why is particles an issue?
Regardless of the cause, area particles is a severe issue.
Larger pieces are simpler to track and prevent however it’s challenging to track pieces smaller sized than 4 inches (10 centimeters). Even little particles can still present a significant risk though. Space particles is typically taking a trip faster than 17,000 miles per hour around theEarth At that speed, pieces of particles might damage any spacecraft or satellite it hit. In the 1980 s, a Soviet satellite separated as an outcome of a presumed particles strike.
More uneasy is the threat particles presents to crewed area objectives. In July 2021, among the International Space Station’s robotic arms was struck by a piece of particles that put a 0.2-inch (0.5 cm) hole tidy through a part of the arm. While the damage did not require to be repaired, authorities identified it as a fortunate strike– if it had actually struck a various part of the station, the scenario might have been a lot even worse.
Space particles is likewise a substantial risk to individuals onEarth Satellites play a crucial function in the international economy through GPS, interactions, and weather condition information. If services such as these were interrupted, there would be considerable financial expense. One research study discovered that a GPS blackout might cost the U.S. as much as $1 billion a day.
There are presently countless pieces of area scrap circling around the Earth, with sources as differed as old rocket bodies, dead satellites, particles from previous accidents and tests, and lost products from astronauts. The issue– like with the environment– is that there is little reward for private nations to prevent creating particles or tidy it up.
The quantity of area particles has actually just increased in time. For years, researchers have actually been cautioning about the possibility of a crash waterfall. As the quantity of particles boosts, the opportunity of accidents in between it and other satellites and particles likewise increases. More accidents may then leave particular orbits totally unusable. While this might take years to play out, occasions like the Russian test will just make such a result most likely.
What to do now?
In the short-term, bit can be done to alleviate this brand-new cloud of area particles, however anybody with anything in area is on high alert to prevent it.
The U.S. federal government and business business are tracking the brand-new particles, and the team on the International Space Station have actually been purchased to keep particular modules shut off as they continue to go through the particles cloud. As the brand-new particles expands and the pieces are tracked, station controllers will have a much better understanding of the threat presented to the team.
In the long term, specialists advise dealing with international options to eliminate particles. This consists of taking steps to avoid particles in the very first location and getting rid of particles that is currently in area. Several governmental and worldwide companies have actually proposed methods to avoid brand-new particles, however these are casual and not lawfully binding.
Remediation is a harder difficulty. Technology to eliminate particles has actually not yet been completely established, however even still, its release is a delicate topic. The exact same innovation that may be utilized to eliminate a piece of area scrap might likewise be utilized for assaulting a satellite. This dual-use innovation presents difficulties, as it can raise suspicions that nations are evaluating anti-satellite weapons under the cover of particles elimination.
Despite the problems, there is growing worldwide acknowledgment that area particles is a hazardous issue. A consortium of personal business just recently developed the Net Zero Space charter to minimize particles, and the U.S. Space Force is searching for methods to fight the issue also. While the world still does not yet have a complete understanding of Russia’s actions, this occasion is a wake-up call on the value of efforts to minimize contamination in Earth’s orbit.
Written by Wendy Whitman Cobb, Professor of Strategy and Security Studies, United States Air Force School of Advanced Air and Space Studies.
This post was very first released in The Conversation.![]()





