Credit: NASA/Jesse Kirsch/ thanks to Tracy Schohr
Today, human sources are accountable for 60% of worldwide methane emissions, coming mostly from the burning of nonrenewable fuel sources, decay in garbage dumps, and the farming sector. Nearly a quarter of methane emissions can be credited to farming, much of which is from raising animals. Rice growing and food waste are likewise essential sources of farming methane, as almost a 3rd of all food produced for human usage is lost or squandered.
At NASA, researchers study the worldwide methane spending plan to much better comprehend the main sources of methane emissions and how they add to environment modification. In addition to the human sources, methane is likewise produced in natural settings. The biggest natural source of methane is wetlands, which contribute 30% of worldwide methane emissions. Other natural sources of methane emissions consist of the oceans, termites, permafrost, plant life, and wildfires.
Atmospheric methane concentrations have more than doubled given that the Industrial Revolution due to the fact that of extensive usage of oil, gas, and coal, increasing need for beef and dairy items, and increased production of food and natural waste. Although the boost in climatic methane concentrations slowed substantially near completion of the 20 th Century, concentrations have actually been increasing significantly given that 2006, most likely as an outcome of increasing emissions from raising animals, restored dependence on gas and, over the last few years, wetlands and worldwide warming.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sdHqQpB50 VY
NASA’s brand-new 3-dimensional picture of methane reveals the world’s second biggest factor to greenhouse warming as it takes a trip through the environment. Combining numerous information sets from emissions stocks and simulations of wetlands into a high-resolution computer system design, scientists now have an extra tool for comprehending this intricate gas and its function in Earth’s carbon cycle, climatic structure, and environment system. The brand-new information visualization constructs a fuller photo of the variety of methane sources on the ground along with the habits of the gas as it moves through the environment. Credit: NASA/Scientific Visualization Studio
The Greenhouse Effect and Methane
Greenhouse gases, consisting of methane, add to chain reactions and environment feedbacks. The greenhouse gas particles trap solar power by imitating a thermal blanket. Energy from the sun is taken in by Earth’s surface area, though a few of this energy is shown into the environment. The taken in energy is likewise re-emitted at infrared wavelengths. Some of the shown and re-emitted energy returns to area, however the rest is caught in the environment by greenhouse gases. Over time, the recorded heat warms our environment, increasing worldwide temperature levels.
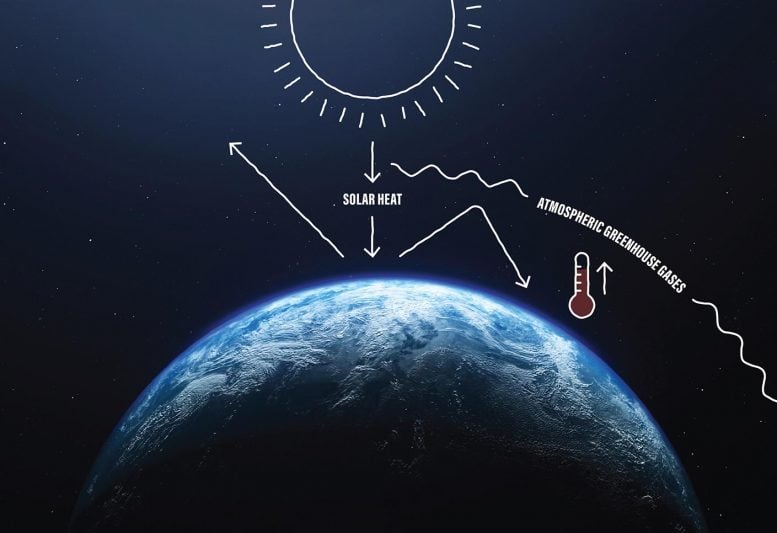
Greenhouse gases in our environment imitate a blanket trapping heat from theSun This triggers worldwide temperature levels to increase as the quantity of greenhouse gases boosts. Credit: NASA/Jesse Kirsch
The human-driven temperature level boosts can have an effect on methane launched from natural sources. For example, permafrost can thaw naturally and discharge methane into the environment, however human beings have actually increased the rate at which permafrost defrosts due to human-caused warming.
Methane is the world’s second biggest factor to worldwide warming, after co2. Although co2 is more plentiful than methane in the environment, a single particle of methane better traps heat than a single particle of co2.
However, the life time of a particle of methane is much shorter than a particle of co2 due to the fact that of natural chemical procedures that are quicker at scrubbing methane out of the environment than co2. This indicates that if methane emissions were to decrease and the natural chemical scrubbing of methane kept, climatic methane might reduce considerably in simply 10 years. Decreasing the quantity of methane took into the environment might have a considerable and almost instant influence on minimizing the near-term results of environment modification and might add to keeping worldwide temperature level modification listed below 2-degrees Celsius
Why Cows Produce Methane
Cattle, such as dairy cows or beef livestock produce methane as a spin-off of food digestion. Cattle are ruminant animals, suggesting they have actually specialized gastrointestinal systems that enable them to process foods that can not be absorbed by human beings and most other animals, like fresh yard and raw grain. When food gets in a bovine’s stomach, it goes through a procedure called enteric fermentation: microorganisms and germs partly break down the food particles, which then ferment in the part of the stomach called the rumen. As the food particles ferment, they produce methane. Every time livestock belch– and, to a smaller sized degree, flatulate– methane is expelled and gets in the environment, where it serves as a greenhouse gas.

Methane quick truths: Methane is accountable for 20% of worldwide warming given that the Industrial Revolution; In 2018, the food system contributed 33% of all human-caused GHG emissions; In 2015, animals added to 10% of United States methane emissions; Methane has to do with 30 times more powerful than CO2 over the period of a century; Europe and the Arctic are the only 2 areas whose methane emissions reduced from 2000 to 2018; Atmospheric methane concentrations have actually more than doubled in the last 200 years. Credit: NASA/Jesse Kirsch
NASA’s Eyes on Methane
While methane concentrations are well observed, emissions need to be presumed based upon a range of aspects. NASA researchers utilize a range of approaches to track methane emissions. To get the most precise price quotes possible, they utilize emissions stocks from nations around the globe, imitate wetland methane emissions, and integrate this with ground-based, air-borne and satellite information utilizing climatic designs.
In California (and some other areas), scientists fly airplane geared up with NASA’s Airborne Visible Infrared Imaging Spectrometer– Next Generation, or AVIRIS-NG, and gather extremely adjusted information. This information is utilized in the California Methane Survey, a job collectively moneyed by NASA, the California Air Resources Board and the California Energy Commission to quickly recognize and report methane leakages.
In Alaska and Northwestern Canada, NASA scientists utilize satellites, airplane and field research study to much better comprehend methane emissions from defrosting permafrost as part of the Arctic Boreal and Vulnerability Experiment, or ABoVE. Researchers have actually found that carbon-rich permafrost is defrosting at significantly high rates, likely as an outcome of human-induced environment modification, making the Arctic a crucial prospective source of methane emissions. According to clinical price quotes, this area’s soils keep 5 times more carbon than has actually been released by all human activities in the last 200 years.
NASA scientists integrate the information from objectives like ABoVE and the California Methane Survey with their understanding of how methane acts in the environment to produce methane computer system designs. These designs can assist researchers and policymakers comprehend previous, present, and future climatic methane patterns.
Paths Toward Reduced Methane Emissions
Researchers in a range of fields have actually checked out prospective services to reduce worldwide methane emissions. For example, biogas systems minimize methane emissions by changing waste from animals, crops, water and food into energy. Biogas is produced through the very same natural procedure that happens in garbage dumps to break down natural waste. However, biogas systems harness the gas that is produced and utilize it as a tidy, sustainable and reputable energy source instead of let it launch into the environment as a greenhouse gas.
A research study led by Professor Ermias Kebreab from the University of California-Davis found that presenting a couple of ounces of seaweed into beef livestock diet plans might minimize their methane emissions by over 82%.
These kinds of technological– and biological– developments might offer decision-makers, ranchers and others with more choices for handling our future methane.





