Arctic sea ice level on March 14, 2024, the day of the yearly optimum.
Arctic sea ice protection in 2024 reduced to 6 million square miles, continuing a 46- year pattern of shrinking and thinning.
Sea ice at the top of the world continued to diminish and thin in2024 The optimum winter season ice protection in the Arctic Ocean follows a continuous 46- year decrease.
Analysis of satellite observations has actually exposed that the overall location of the Arctic Ocean covered in sea ice reached 6 million square miles (1565 million square kilometers) on March14 That’s 247,000 square miles (640,000 square kilometers) less ice than the typical optimum level in between 1981 and2010 Overall, the optimum winter season ice protection in the Arctic has actually diminished by a location equivalent to the size of Alaska considering that 1979.
The map above reveals the ice level on March 14, the day of the yearly optimum. To figure out level, researchers job satellite observations of sea ice onto a grid and after that accumulate the overall location of each cell that is at least 15 percent ice-covered. The yellow summary reveals the mean sea ice level for February from 1981 to2010 A mean is the middle worth; that is, half of the levels were bigger than the yellow line and half were smaller sized.
The analysis is based upon information gathered with microwave sensing units aboard the Nimbus -7 satellite, collectively run by < period class ="glossaryLink" aria-describedby ="tt" data-cmtooltip ="<div class=glossaryItemTitle>NASA</div><div class=glossaryItemBody>Established in 1958, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is an independent agency of the United States Federal Government that succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA). It is responsible for the civilian space program, as well as aeronautics and aerospace research. Its vision is "To discover and expand knowledge for the benefit of humanity." Its core values are "safety, integrity, teamwork, excellence, and inclusion." NASA conducts research, develops technology and launches missions to explore and study Earth, the solar system, and the universe beyond. It also works to advance the state of knowledge in a wide range of scientific fields, including Earth and space science, planetary science, astrophysics, and heliophysics, and it collaborates with private companies and international partners to achieve its goals.</div>" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex ="0" function ="link" > NASA and theNationalOceanic andAtmospheric Administration( < period class ="glossaryLink" aria-describedby ="tt" data-cmtooltip ="<div class=glossaryItemTitle>NOAA</div><div class=glossaryItemBody>The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) is a scientific agency of the United States government that is focused on understanding and predicting changes in Earth's oceans, atmosphere, and climate. It is headquartered in Silver Spring, Maryland and is a part of the Department of Commerce. NOAA conducts research and provides information, products, and services that are used to protect life and property, and to support economic growth and development. It also works to conserve and manage natural resources, including fisheries, wildlife, and habitats. Some of the specific activities that NOAA is involved in include weather forecasting, climate monitoring, marine biology and fisheries research, and satellite and remote sensing.</div>" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex ="0" function ="link" > NOAA), together with satellites in theDefenseMeteorologicalSatelliteProgram
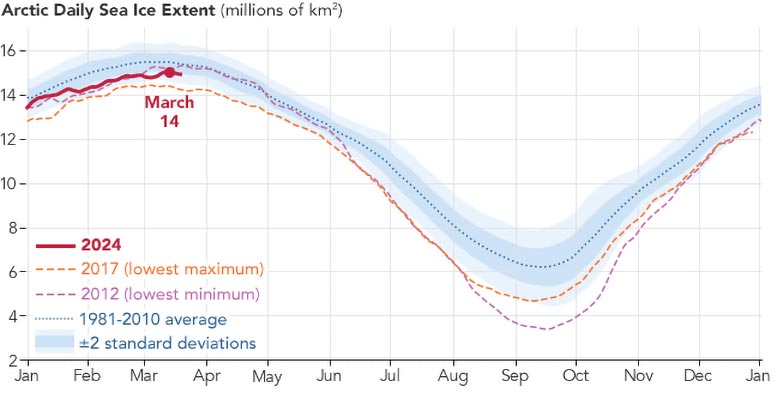
Daily sea ice level throughMarch (****************************************************************************** ), 2024, (red) compared to the 2017 record low( orange) and the typical level from1981 to2010( blue).(********** )(*********** )
This chart reveals the day-to-day sea ice level through mid- March(********************************************************** )( red) compared to the 2017 record low( orange) and the typical level from1981 to2010 (blue).This year’sArctic ice optimum is the 14 th least expensive on record.Complex weather condition patterns make it hard to anticipate what will take place in any given year.
Scientists with NASA and theNationalSnow andIceDataCenter( NSIDC) at theUniversity ofColorado,Boulder, track these seasonal and yearly changes since sea ice shapes Earth’s polar communities and plays a substantial function in international environment.
“The sea ice and the snow on top of it are very reflective,” stated ice researcher Linette Boisvert of NASA’s Goddard Space FlightCenter “In the summer, if we have more sea ice, it reflects the Sun’s radiation and helps keep the planet cooler.”
Conversely, diminishing ice makes Earth more prone to solar heating. The exposed ocean is darker and easily takes in solar radiation, catching and keeping that energy and eventually adding to warming in the world’s oceans and environment.
Sea ice around the poles is more prone to the weather condition than it was a lots years back. Ice density measurements gathered with laser altimeters aboard NASA’s ICESat-2 satellite reveal that less ice has actually handled to remain through the warmer months. This indicates brand-new ice should form from scratch each year, instead of structure on old ice to make thicker layers. Thinner ice, in turn, is more susceptible to melting than multi-year build-ups.
“The thought is that in a couple of decades, we’re going to have these essentially ice-free summers,” Boisvert stated, with ice protection decreased listed below 400,000 square miles (1 million square kilometers) and the majority of the Arctic Ocean exposed to the Sun’s warming glare.
NASA Earth Observatory images by Lauren Dauphin, utilizing information from the National Snow and Ice DataCenter Story by James Riordon/ NASA’s Earth Science News Team, adjusted for Earth Observatory.





