The Federal Reserve on Wednesday raised its benchmark rates of interest to the greatest level in 15 years, suggesting the battle versus inflation is not over in spite of some appealing indications recently.
Keeping with expectations, the rate-setting Federal Open Market Committee voted to increase the over night interest rate half a portion point, taking it to a targeted variety in between 4.25% and 4.5%. The boost broke a string of 4 straight three-quarter point walkings, the most aggressive policy relocations because the early 1980 s.
associated investing news


Along with the boost came a sign that authorities anticipate to keep rates greater through next year, without any decreases till2024 The anticipated “terminal rate,” or point where authorities anticipate to end the rate walkings, was put at 5.1%, according to the FOMC’s “dot plot” of specific members’ expectations.
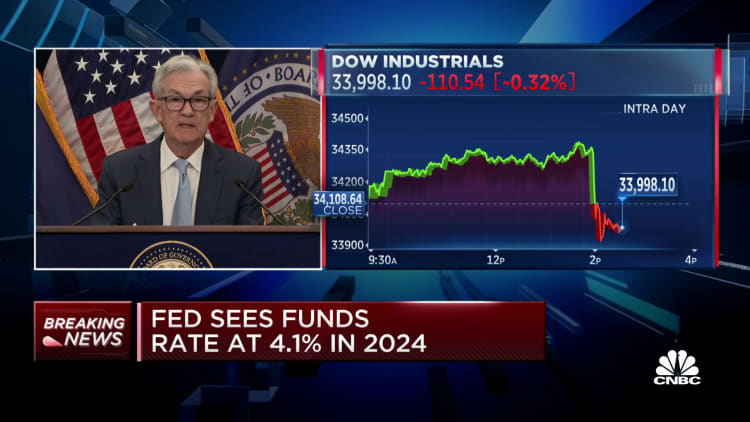
Investors at first responded adversely to the expectation that rates might remain greater for longer, and stocks quit earlier gains. During a press conference, Chairman Jerome Powell stated it was very important to maintain the battle versus inflation so that the expectation of greater rates does not end up being established.
“Inflation data received so far for October and November show a welcome reduction in the monthly pace of price increases,” the chair stated at his post-meeting press conference. “But it will take substantially more evidence to have confidence that inflation is on a sustained downward” course.
The brand-new level marks the greatest the fed funds rate has actually been because December 2007, simply ahead of the international monetary crisis and as the Fed was loosening up policy strongly to fight what would become the worst financial recession because the Great Depression.
This time around, the Fed is raising rates into what is anticipated to be a moribund economy in 2023.
Members booked boosts for the funds rate till it strikes an average level of 5.1% next year, comparable to a target variety of 5% -5.25 At that point, authorities are most likely to stop briefly to permit the effect of financial policy tightening up to make its method through the economy.
The agreement then indicated a complete portion point worth of rate cuts in 2024, taking the funds rate to 4.1% by the end of that year. That is followed by another portion point of cuts in 2025 to a rate of 3.1%, prior to the benchmark settles into a longer-run neutral level of 2.5%.
However, there was a relatively large dispersion in the outlook for future years, suggesting that members doubt about what is ahead for an economy handling the worst inflation it has actually seen because the early 1980 s.
The most recent dot plot included numerous members seeing rates heading significantly greater than the mean point for 2023 and2024 For 2023, 7 of the 19 committee members– citizens and nonvoters consisted of– saw rates increasing above 5.25%. Similarly, there were 7 members who saw rates greater than the mean 4.1% in 2024.
The FOMC policy declaration, authorized all, was essentially the same from November’s conference. Some observers had actually anticipated the Fed to modify language that it sees “ongoing increases” ahead to something less committal, however that expression stayed in the declaration.
Fed authorities think raising rates assists take cash out the economy, decreasing need and eventually pulling rates lower after inflation increased to its greatest level in more than 40 years.
The FOMC reduced its development targets for 2023, putting anticipated GDP gains at simply 0.5%, hardly above what would be thought about an economic downturn. The GDP outlook for this year likewise was put at 0.5%. In the September forecasts, the committee anticipated 0.2% development this year and 1.2% next.
The committee likewise raised its mean quote for its preferred core inflation procedure to 4.8% for 2022, up 0.3 portion point from the September outlook. Members a little reduced their joblessness rate outlook for this year and bumped it a bit greater for the occurring years.
The rate walking follows successive reports revealing development in the inflation battle.
The Labor Department reported Tuesday that the customer rate index increased simply 0.1% in November, a smaller sized boost than anticipated as the 12- month rate dropped to 7.1%. Excluding food and energy, the core CPI rate was at 6%. Both procedures were the most affordable because December2021 A level the Fed puts more weight on, the core individual intake expenses rate index, was up to a 5% yearly rate in October.
However, all of those readings stay well above the Fed’s 2% target. Officials have actually worried the requirement to see constant decreases in inflation and have actually cautioned versus relying excessive on patterns over simply a couple of months.
Powell stated the current news was welcome however he still sees services inflation as too expensive.
“There’s an expectation really that the services inflation will not move down so quickly, so we’ll have to stay at it,” he stated. “We may have to raise rates higher to get where we want to go.”
Central lenders still feel they have freedom to raise rates, as hiring stays strong and customers, who drive about two-thirds of all U.S. financial activity, are continuing to invest.
Nonfarm payrolls grew by a faster-than-expected 263,000 in November, while the Atlanta Fed is tracking GDP development of 3.2% for the 4th quarter. Retail sales grew 1.3% in October and were up 8.3% on a yearly basis, suggesting that customers up until now are weathering the inflation storm.
Inflation happened from a merging of a minimum of 3 elements: Outsized need for products throughout the pandemic that produced serious supply chain concerns, Russia’s intrusion of Ukraine that accompanied a spike in energy rates, and trillions in financial and financial stimulus that produced an excess of dollars trying to find a location to go.
After costs much of 2021 dismissing the rate increases as “transitory,” the Fed began raising rates of interest in March of this year, very first tentatively and after that more strongly, with the previous 4 boosts in 0.75 portion point increments. Prior to this year, the Fed had actually not raised rates more than a quarter point at a time in 22 years.
The Fed likewise has actually been participated in “quantitative tightening,” a procedure in which it is enabling earnings from growing bonds to roll off its balance sheet every month instead of reinvesting them.
A capped overall of $95 billion is being enabled to run every month, leading to a $332 billion decrease in the balance sheet because earlyJune The balance sheet now stands at $8.63 trillion.





