An artist’s principle of NASA’s Advanced Composite Solar Sail System spacecraft in orbit as the Sun crests Earth’s horizon. Credit: NASA/Aero Animation/Ben Schweighart
< period class ="glossaryLink" aria-describedby ="tt" data-cmtooltip ="<div class=glossaryItemTitle>NASA</div><div class=glossaryItemBody>Established in 1958, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is an independent agency of the United States Federal Government that succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA). It is responsible for the civilian space program, as well as aeronautics and aerospace research. Its vision is "To discover and expand knowledge for the benefit of humanity." Its core values are "safety, integrity, teamwork, excellence, and inclusion." NASA conducts research, develops technology and launches missions to explore and study Earth, the solar system, and the universe beyond. It also works to advance the state of knowledge in a wide range of scientific fields, including Earth and space science, planetary science, astrophysics, and heliophysics, and it collaborates with private companies and international partners to achieve its goals.</div>" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex ="0" function ="link" > NASA‘sAdvanced CompositeSolarSailSystem Mission is on its method!The spacecraft took off from the launch pad aboard RocketLab’sElectron rocket at the business’sLaunchComplex 1 in Māhia,NewZealand at10:33 a.m. onApril24NewZealand time.
The microwave oven-sized satellite is on its method to lowEarth orbit to evaluate its next-generation solar sail innovation, utilizing the power of sunshine as propulsion.
SolarSailTechnology
(************** )Sailing through area may seem like something out of sci-fi, however the principle is no longer restricted to books or the cinema. A next-generation solar sail innovation– called theAdvancedCompositeSolarSailSystem– simply introduced aboard aRocket LabElectron rocket.The innovation might advance future area travel and broaden our understanding of ourSun and planetary system.
Solar cruises utilize the pressure of sunshine for propulsion, angling towards or far from theSun so that photons bounce off the reflective sail to press a spacecraft.(****************************************************************************************************************************************** )removes heavy propulsion systems and might make it possible for longer period and lower-cost objectives.Although mass is minimized, solar sails have actually been restricted by the product and structure of the booms, which act just like a sailboat’s mast.(*********************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************** )NASA will alter the cruising video game for the future.
NASA’s New Lightweight Sailor
The Advanced Composite Solar Sail System presentation utilizes a twelve-unit (12 U) CubeSat constructed by NanoAvionics to evaluate a brand-new composite boom made from versatile polymer and carbon fiber products that are stiffer and lighter than previous boom styles. The objective’s main goal is to effectively show brand-new boom implementation, once released, the group likewise wants to show the sail’s efficiency.
Like a sailboat turning to catch the wind, the solar sail can change its orbit by angling its sail. After assessing the boom implementation, the objective will evaluate a series of maneuvers to alter the spacecraft’s orbit and collect information for prospective future objectives with even bigger sails.
“Booms have tended to be either heavy and metallic or made of lightweight composite with a bulky design – neither of which work well for today’s small spacecraft. Solar sails need very large, stable, and lightweight booms that can fold down compactly,” stated Keats Wilkie, the objective’s primary detective at NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton,Virginia “This sail’s booms are tube-shaped and can be squashed flat and rolled like a tape measure into a small package while offering all the advantages of composite materials, like less bending and flexing during temperature changes.”
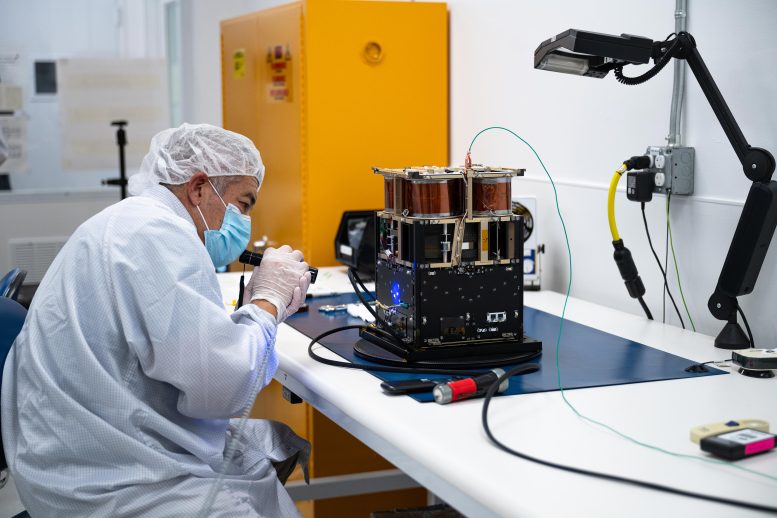

Mariano Perez, quality control engineer at NASA Ames, checks the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System spacecraft. When the composite booms and solar sail release in orbit, they will determine about 860 square feet (80 square meters)– about the size of 6 parking areas. Credit: NASA/Brandon Torres
Deployment and Visibility of the Solar Sail
After reaching its Sun- simultaneous orbit, about 600 miles (1,000 kilometers) above Earth, the spacecraft will start unrolling its composite booms, which cover the diagonals of the polymer sail. After around 25 minutes the solar sail will totally release, determining about 860 square feet (80 square meters)– about the size of 6 parking areas. Spacecraft- installed cams will catch the sail’s huge minute, monitoring its shape and balance throughout implementation.
With its big sail, the spacecraft might show up from Earth if the lighting conditions are ideal. Once totally broadened and at the correct orientation, the sail’s reflective product will be as intense as Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky.
“Seven meters of the deployable booms can roll up into a shape that fits in your hand,” stated Alan Rhodes, the objective’s lead systems engineer at NASA’s Ames Research Center in California’s SiliconValley “The hope is that the new technologies verified on this spacecraft will inspire others to use them in ways we haven’t even considered.”
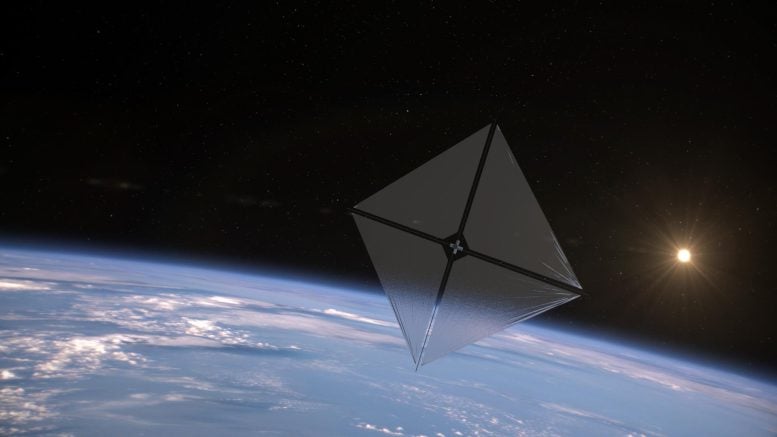

This artist’s principle reveals the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System spacecraft cruising in area utilizing the energy of theSun Credit: NASA/Aero Animation/Ben Schweighart
Enabling Future Innovations
Through NASA’s Small Spacecraft Technology program, effective implementation and operation of the solar sail’s light-weight composite booms will show the ability and unlock to bigger scale objectives to the Moon, < period class ="glossaryLink" aria-describedby ="tt" data-cmtooltip ="<div class=glossaryItemTitle>Mars</div><div class=glossaryItemBody>Mars is the second smallest planet in our solar system and the fourth planet from the sun. It is a dusty, cold, desert world with a very thin atmosphere. Iron oxide is prevalent in Mars' surface resulting in its reddish color and its nickname "The Red Planet." Mars' name comes from the Roman god of war.</div>" data-gt-translate-attributes= "[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex ="0" function ="link" >Mars, and beyond.
This boom style might possibly support future solar sails as big as 5,400 square feet(500 square meters), about the size of a basketball court, and innovation arising from the objective’s success might support sails of as much as21,500 square feet( 2, 000 square meters)– about half a soccer field.
“The Sun will continue burning for billions of years, so we have a limitless source of propulsion. Instead of launching massive fuel tanks for future missions, we can launch larger sails that use “fuel” currently offered,” statedRhodes“We will demonstrate a system that uses this abundant resource to take those next giant steps in exploration and science.”
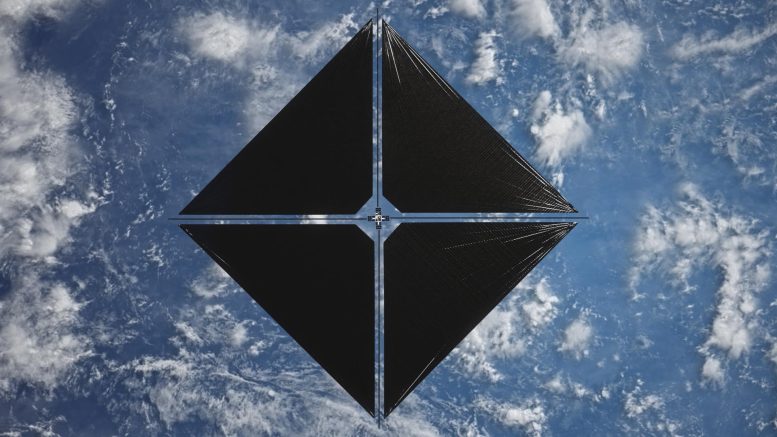
NASA’sAdvancedCompositeSolarSailSystem was introduced as a secondary payload aboardRocket Lab’s‘Beginning of the Swarm’ objective.TheSolarSail System will show making use of ingenious products and structures to release a next-generation solar sail from a microwave-sized CubeSat.Just as a sailboat is powered by wind in a sail, solar sails utilize the pressure of sunshine for propulsion, removing the requirement for standard rocket propellant. Credit: NASA
Because the sails utilize the power of the Sun, they can offer continuous thrust to support objectives that need special perspective, such as those that look for to comprehend our Sun and its influence onEarth Solar sails have actually long been a wanted ability for objectives that might bring early caution systems for keeping an eye on solar weather condition. Solar storms and coronal mass ejections can trigger significant damage on Earth, overwhelming power grids, interrupting radio interactions, and impacting airplane and spacecraft.
Composite booms may likewise have a future beyond solar cruising: the light-weight style and compact packaging system might make them the ideal product for building environments on the Moon and Mars, serving as framing structures for structures or compact antenna poles to produce an interactions relay for astronauts checking out the lunar surface area.
“This technology sparks the imagination, reimagining the whole idea of sailing and applying it to space travel,” stated Rudy Aquilina, job supervisor of the solar sail objective at NASAAmes “Demonstrating the abilities of solar sails and lightweight, composite booms is the next step in using this technology to inspire future missions.”
NASA Ames handles the Advanced Composite Solar Sail System job and developed and constructed the onboard cam diagnostic system. NASA Langley developed and constructed the deployable composite booms and solar sail system. NASA’s Small Spacecraft Technology (SST) program workplace based at NASA Ames and led by the company’s Space Technology Mission Directorate (STMD), funds and handles the objective. NASA STMD’sGame Changing Development program established the deployable composite boom innovation. Rocket Lab U.S.A., Inc ofLong Beach, California is supplying launch services. NanoAvionics is supplying the spacecraft bus.





