Sea level increase is impacting seaside neighborhoods around the globe, specifically those like Honolulu, visualized, that lie on islands. Credit: NOAA Teacher at Sea Program, NOAA Ship HI’IALAKAI
A long-lasting water level dataset reveals ocean surface area heights continuing to increase at faster and much faster rates over years of observations.
Global typical water level increased by about 0.3 inches (0.76 centimeters) from 2022 to 2023, a fairly big dive due mainly to a warming environment and the advancement of a strong El Ni ño. The overall increase is comparable to draining pipes a quarter of Lake Superior into the ocean throughout a year.
This < period class ="glossaryLink" aria-describedby ="tt" data-cmtooltip ="<div class=glossaryItemTitle>NASA</div><div class=glossaryItemBody>Established in 1958, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is an independent agency of the United States Federal Government that succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA). It is responsible for the civilian space program, as well as aeronautics and aerospace research. Its vision is "To discover and expand knowledge for the benefit of humanity." Its core values are "safety, integrity, teamwork, excellence, and inclusion." NASA conducts research, develops technology and launches missions to explore and study Earth, the solar system, and the universe beyond. It also works to advance the state of knowledge in a wide range of scientific fields, including Earth and space science, planetary science, astrophysics, and heliophysics, and it collaborates with private companies and international partners to achieve its goals.</div>" data-gt-translate-attributes="(** )" tabindex ="0" function ="link" > NASA– led analysis is based upon a water level dataset including more than30 years of satellite observations, beginning with the U.S.- French TOPEX/Poseidon objective, which released in 1992.The(********************************************************************************************************************** )-6Michael Freilich objective, which released in(********************************************************************************************************************************* )2020, is the most recent in the series of satellites that have actually added to this water level record.
The information reveals that international typical water level has actually increased an overall of about 4 inches( 9.4 centimeters) given that1993The rate of this boost has actually likewise sped up, more than doubling from 0.07 inches( 0.18 centimeters) annually in1993 to the present rate of 0.17 inches( 0.42 centimeters) annually.
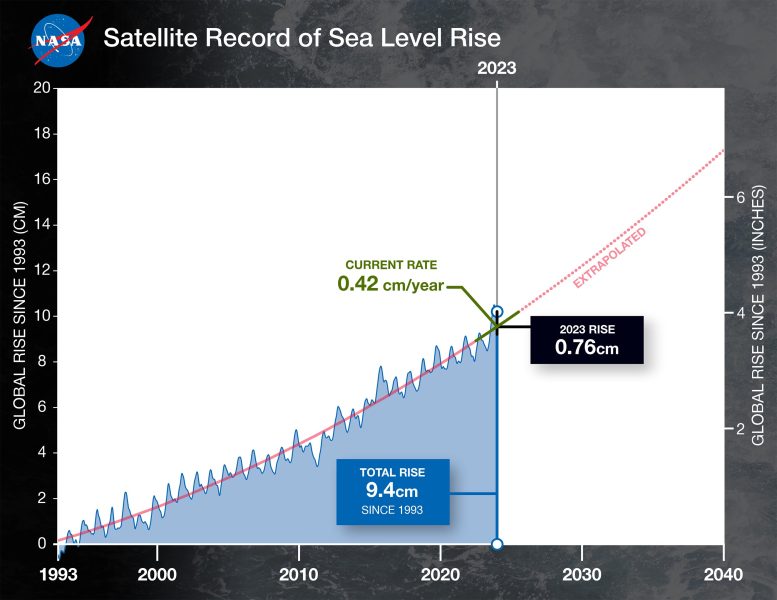
This chart reveals international mean sea level (in blue) given that 1993 as determined by a series of 5 satellites.(********************************************************************************************************** )strong red line shows the trajectory of this boost, which more than folded the previous 3 years.The dotted red line tasks future water level increase.Credit: NASA-JPL/Caltech
“Current rates of acceleration mean that we are on track to add another 20 centimeters of global mean sea level by 2050, doubling the amount of change in the next three decades compared to the previous 100 years and increasing the frequency and impacts of floods across the world,” statedNadyaVinogradova Shiffer, director for the NASA water level modification group and the ocean physics program inWashington
SeasonalEffects
Global water level saw a substantial dive from2022 to2023 due primarily to a switch in betweenLaNi ña andEl(********************************************************************************************************************************** )ño conditions. A moderateLaNi ña from2021 to(********************************************************************* )led to a lower-than-expected increase in water level that year. A strong El Ni ño established in 2023, assisting to enhance the typical quantity of increase in sea surface area height.
La Ni ña is defined by cooler-than-normal ocean temperature levels in the equatorial PacificOcean El Ni ño includes warmer-than-average ocean temperature levels in the equatorialPacific Both regular environment phenomena impact patterns of rains and snowfall in addition to water level around the globe.
“During La Niña, rain that normally falls in the ocean falls on the land instead, temporarily taking water out of the ocean and lowering sea levels,” stated Josh Willis, a water level scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in SouthernCalifornia “In El Niño years, a lot of the rain that normally falls on land ends up in the ocean, which raises sea levels temporarily.”
This animation reveals the increase in international mean sea level from 1993 to 2023 based upon information from a series of 5 worldwide satellites. The spike in water level from 2022 to 2023 is mainly an effect of environment modification and the advancement of El Ni ño conditions in the Pacific Ocean.
A Human Footprint
Seasonal or regular environment phenomena can impact international typical water level from year to year. But the hidden pattern for more than 3 years has actually been increasing ocean heights as a direct action to international warming due to the extreme heat caught by greenhouse gases in Earth’s environment.
“Long-term datasets like this 30-year satellite record allow us to differentiate between short-term effects on sea level, like El Niño, and trends that let us know where sea level is heading,” stated Ben Hamlington, lead for NASA’s water level modification group at < period class ="glossaryLink" aria-describedby ="tt" data-cmtooltip ="<div class=glossaryItemTitle>JPL</div><div class=glossaryItemBody>The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a federally funded research and development center that was established in 1936. It is owned by NASA and managed by the California Institute of Technology (Caltech). The laboratory's primary function is the construction and operation of planetary robotic spacecraft, though it also conducts Earth-orbit and astronomy missions. It is also responsible for operating NASA's Deep Space Network. JPL implements programs in planetary exploration, Earth science, space-based astronomy and technology development, while applying its capabilities to technical and scientific problems of national significance.</div>" data-gt-translate-attributes="(** )" tabindex ="0" function ="link" > JPL
(********************************************************************************************************* )multidecadal observations would not be possible without continuous worldwide cooperation, in addition to clinical and technical developments by NASA and other area firms. Specifically, radar altimeters have actually assisted produce ever-more exact measurements of water level around the globe.(******************************************************************************************************* )compute ocean height, these instruments bounce microwave signals off the sea surface area, taping the time the signal requires to take a trip from a satellite toEarth and back, in addition to the strength of the return signal.
The scientists likewise regularly cross-check those water level measurements versus information from other sources. These consist of tide evaluates, in addition to satellite measurements of elements like climatic water vapor and Earth’s gravity field that can impact the < period class ="glossaryLink" aria-describedby ="tt" data-cmtooltip =(************************************************************* )data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex ="0" function ="link" > precision of water level measurements. Using that details, the scientists recalibrated the30- year dataset, leading to updates to water level in some previous years.That consists of a water level rise boost of 0.08 inches( 0.21 centimeters) from2021 to(********************************************************************* ).
(************************************************************************************************** )scientists integrate space-based altimetry information of the oceans with more than a century of observations from surface-based sources, such as tide evaluates, the details drastically enhances our understanding of how sea surface area height is altering on an international scale. When these water level measurements are integrated with other details, consisting of ocean temperature level, ice loss, and land movement, researchers can figure out why and how seas are increasing.





