In this illustration, NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter bases on the Red Planet’s surface area as NASA’s Perseverance rover (partly noticeable left wing) rolls away. It finished its 50 th flight on April 13, 2023, covering over 1,057 feet and reaching a brand-new elevation record of 59 feet. Initially developed for just 5 flights, Ingenuity has actually gone beyond expectations, supplying indispensable flight information and images for future Mars objectives. While some elements reveal indications of wear, Ingenuity’s objective continues to press the limitations of innovation and expedition onMars Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
The history-making rotorcraft has actually just recently been working out a few of the most harmful surface it’s come across on the Red Planet.
< period class ="glossaryLink" aria-describedby ="tt" data-cmtooltip ="<div class=glossaryItemTitle>NASA</div><div class=glossaryItemBody>Established in 1958, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is an independent agency of the United States Federal Government that succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA). It is responsible for the civilian space program, as well as aeronautics and aerospace research. Its vision is "To discover and expand knowledge for the benefit of humanity." Its core values are "safety, integrity, teamwork, excellence, and inclusion." NASA conducts research, develops technology and launches missions to explore and study Earth, the solar system, and the universe beyond. It also works to advance the state of knowledge in a wide range of scientific fields, including Earth and space science, planetary science, astrophysics, and heliophysics, and it collaborates with private companies and international partners to achieve its goals.</div>" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{" attribute="">NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter marked its 50th flight on April 13, 2023, achieving new altitude and distance records. Despite facing challenging terrain and increased frequency of flights, Ingenuity continues to provide valuable data for future Mars missions.
NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter has completed its 50th flight on Mars. The first aircraft on another world reached the half-century mark on April 13, traveling over 1,057.09 feet (322.2 meters) in 145.7 seconds. The helicopter also achieved a new altitude record of 59 feet (18 meters) before alighting near the half-mile-wide (800-meter-wide) “Belva Crater.”

Ingenuity at Airfield D: This image of NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was taken by the Mastcam-Z instrument of the Perseverance rover on June 15, 2021, the 114th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The location, “Airfield D” (the fourth airfield), is just east of the “Séítah” geologic unit. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU/MSSS
With Flight 50 in the mission logbook, the helicopter team plans to perform another repositioning flight before exploring the “Fall River Pass” region of Jezero Crater.
“Just as the Wright brothers continued their experiments well after that momentous day at Kitty Hawk in 1903, the Ingenuity team continues to pursue and learn from the flight operations of the first aircraft on another world,” said Lori Glaze, director of the Planetary Science Division at NASA Headquarters in Washington.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9qGtuh17 OEg
NASA’s Ingenuity Mars helicopter made history when it accomplished the very first powered, managed flight on another world on April 19,2021 A little less than 2 years later on, on April 13, 2023, it finished its 50 th flight. Here are some highlights from the rotorcraft’s journeys on the RedPlanet Credit: NASA/< period class ="glossaryLink" aria-describedby ="tt" data-cmtooltip ="<div class=glossaryItemTitle>JPL</div><div class=glossaryItemBody>The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a federally funded research and development center that was established in 1936. It is owned by NASA and managed by the California Institute of Technology (Caltech). The laboratory's primary function is the construction and operation of planetary robotic spacecraft, though it also conducts Earth-orbit and astronomy missions. It is also responsible for operating NASA's Deep Space Network. JPL implements programs in planetary exploration, Earth science, space-based astronomy and technology development, while applying its capabilities to technical and scientific problems of national significance.</div>" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{" attribute="">JPL-Caltech/ASU/MSSS
Ingenuity landed on the Red Planet in February 2021 attached to the belly of NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover and will soon mark the two-year anniversary of its first flight, which took place on April 19, 2021. Designed as a technology demonstration that would fly no more than five times, the helicopter was intended to prove powered, controlled flight on another planet was possible. But Ingenuity exceeded expectations and transitioned into being an operations demonstration.
Every time Ingenuity goes airborne, it covers new ground and offers a perspective no previous planetary mission could achieve. Imagery from the helicopter has not only demonstrated how aircraft could serve as forward scouts for future planetary expeditions, but it has even come in handy for the Perseverance team.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gr27 h6qkUHQ
Teddy Tzanetos at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory supplies an upgrade on the firm’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter and talks about how it’s motivating future aerial expedition of the RedPlanet Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
By evaluating the helicopter’s limitations, engineers are collecting flight information that can be utilized by engineers dealing with styles for possible future Mars helicopters. That consists of individuals creating the Mars Sample Return project’s proposed Sample Recovery Helicopters.
Riskier Terrain
Since leaving the reasonably flat boundaries of Jezero Crater’s flooring on January 19, Ingenuity has actually flown 11 times, setting brand-new speed and elevation records of 14.5 miles per hour (6.5 meters per second) and 59 feet (18 meters) along the method.
Although the deep chill of winter season and local dust occasions (which can obstruct the Sun’s rays from reaching the helicopter’s photovoltaic panel) have actually eased off, Ingenuity continues to brown out in the evening. As an outcome, the Helicopter Base Station on the rover requires to look for the rotorcraft’s signal each early morning at the time Ingenuity is anticipated to get up. And when the helicopter does fly, it now should browse rugged and reasonably uncharted surface, landing in areas that can be surrounded by threats.
NASA’s Ingenuity Mars Helicopter is seen here at the beginning point of its 47 th flight onMars The video was caught by the Mastcam- Z imager aboard NASA’s Perseverance rover on March 9,2023 Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/ ASU/MSSS
“We are not in Martian Kansas anymore,” stated Josh Anderson, Ingenuity operations lead at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in SouthernCalifornia “We’re flying over the dried-up remnants of an ancient river that is filled with sand dunes, boulders, and rocks, and surrounded by hills that could have us for lunch. And while we recently upgraded the navigation software onboard to help determine safe airfields, every flight is still a white-knuckler.”
Frequent Flyer
Beyond dealing with more difficult surface, Ingenuity will likewise fly at a higher frequency in the coming days due to the fact that the helicopter requires to stay within electronic earshot of the rover. With its AutoNav ability, Perseverance can take a trip numerous meters every day.
“Ingenuity relies on Perseverance to act as a communications relay between it and mission controllers here at JPL,” statedAnderson “If the rover gets too far ahead or disappears behind a hill, we could lose communications. The rover team has a job to do and a schedule to keep. So it’s imperative Ingenuity keeps up and is in the lead whenever possible.”
Perseverance just recently finished checking out “Foel Drygarn,” a clinical target that might consist of hydrated silica (which is of strong astrobiological interest). It is presently headed to “Mount Julian,” which will supply a breathtaking view into neighboring Belva Crater.

Illustration of NASA’s Ingenuity helicopter onMars Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Feats of Ingenuity
Built with lots of off-the-shelf elements, such as smart device processors and video cameras, Ingenuity is now 23 Earth months and 45 flights beyond its anticipated life time. The rotorcraft has actually flown for over 89 minutes and more than 7.1 miles (116 kilometers).
“When we first flew, we thought we would be incredibly lucky to eke out five flights,” stated Teddy Tzanetos, Ingenuity group lead at JPL. “We have exceeded our expected cumulative flight time since our technology demonstration wrapped by 1,250% and expected distance flown by 2,214%.”
Surpassing expectations like this comes at an expense, nevertheless. With some helicopter elements revealing indications of wear and the surface ending up being more difficult, the Ingenuity group acknowledges that every fantastic objective should ultimately pertain to an end. “We have come so far, and we want to go farther,” statedTzanetos “But we have known since the very beginning our time at Mars was limited, and every operational day is a blessing. Whether Ingenuity’s mission ends tomorrow, next week, or months from now is something no one can predict at present. What I can predict is that when it does, we’ll have one heck of a party.”
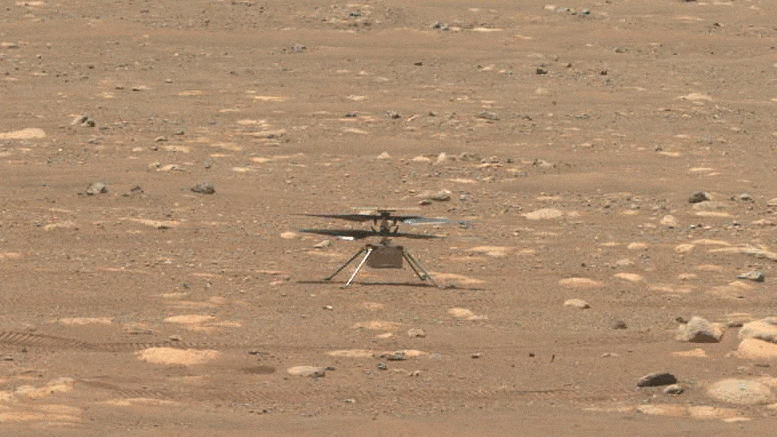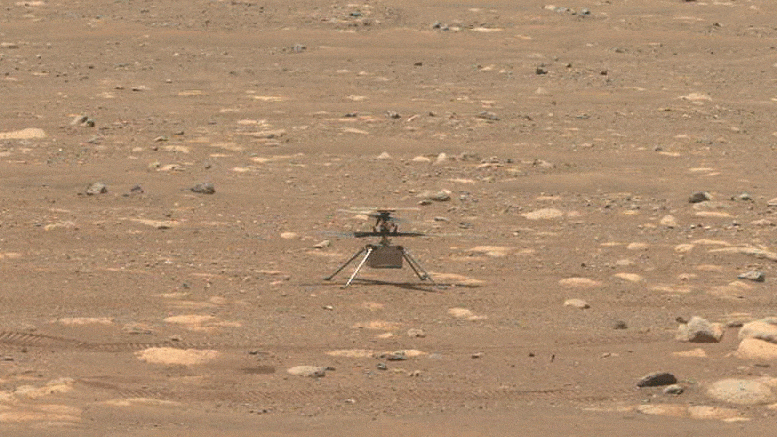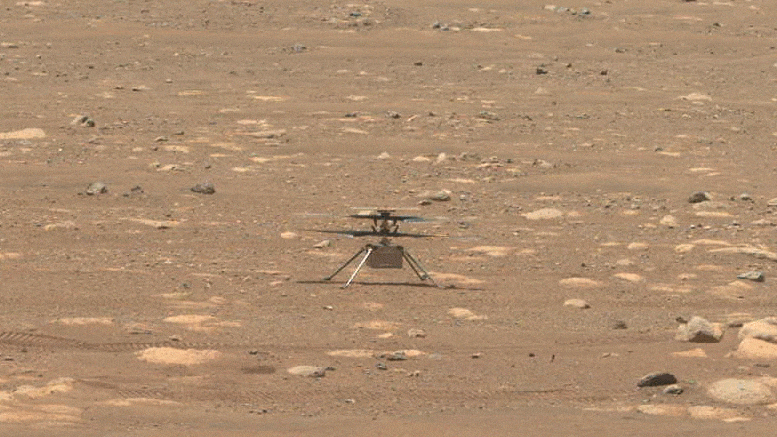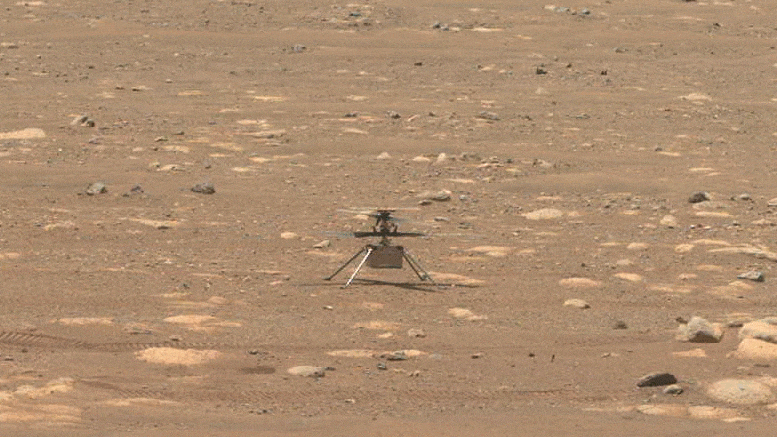
NASA’s Ingenuity helicopter does a sluggish spin test of its blades, on April 8, 2021, the 48 th Martian day, or sol, of the objective. This image was caught by the Navigation Cameras on NASA’s Perseverance Mars rover. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech
More About Ingenuity
JPL (Jet Propulsion Laboratory) built the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter and manages the task on behalf of NASAHeadquarters Support for the undertaking originates from NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, with NASA’s Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley, California, and NASA’s Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, contributing significant flight efficiency analysis and technical assistance throughout the advancement ofIngenuity Companies such as AeroVironment Inc., Qualcomm, and So lAero likewise provided their knowledge in style and provided crucial automobile elements. The Mars Helicopter Delivery System was developed and produced by Lockheed Space.
At the helm of the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter program at NASA Headquarters is Dave Lavery, working as the program executive.





