Credit: NASA Worldview
The year 2020 will be kept in mind for being a really attempting year and western wildfires have actually simply contributed to the year’s problems. So far in 2020, California has actually experienced 7,606 fires and those fires have actually taken in 2.3 million acres. Washington and Oregon have actually likewise been hard struck by wildfires. Over 300,000 acres are reported to be burning. Four towns in Oregon have actually been primarily ruined by the wildfire destruction. The town of Malden in Washington was likewise ruined. And a wildfire meteorologist with the National Interagency Fire Center, Nick Nausler, tweeted that the U.S. has actually not seen this level of wildfire activity considering that the “Big Blowup” of 1910.
Credit: NASA Worldview
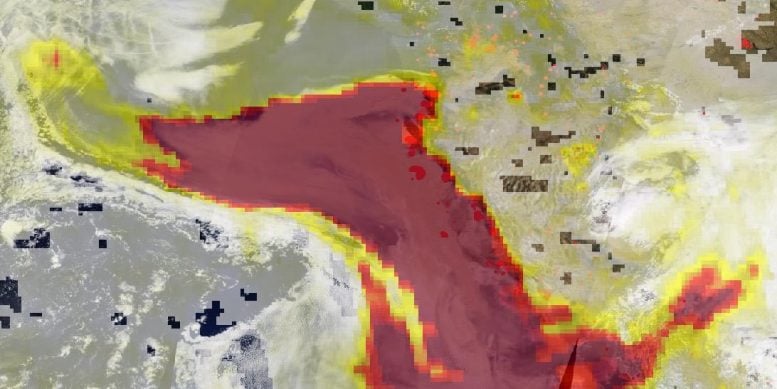
In the images above, the leading image reveals the locations (marked in red) where the wildfires are presently burning in the West. Copious quantities of smoke spill off the coast and into the Pacific Ocean. Thee 2nd image, nevertheless, reveals the genuine story of the threat that smoke postures. Using the OMPS (Ozone Mapping Profiler Suite) instrument aerosols are found and determined in regards to density and height of the climatic aerosol layer. For most climatic occasions including aerosols, the AI varies from 0.0 (colorless through light yellow, yellow, orange, and red) to 5.0 (crimson), with 5.0 suggesting heavy concentrations of aerosols that might minimize presences or effect health. High aerosol concentrations not just can impact environment and minimize exposure, they likewise can affect breathing, recreation, the cardiovascular system, and the main nerve system, according to the United States EPA. Since aerosols have the ability to stay suspended in the environment and be brought in dominating high-altitude wind streams, they can take a trip country miles far from their source and their impacts can remain as evidenced in the image discovered listed below.
The smoke launched by any kind of fire (forest, brush, crop, structure, tires, waste or wood burning) is a mix of particles and chemicals produced by insufficient burning of carbon-containing products. All smoke includes carbon monoxide gas, co2, and particle matter (PM or soot). Smoke can consist of various chemicals, consisting of aldehydes, acid gases, sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, polycyclic fragrant hydrocarbons (PAHs), benzene, toluene, styrene, metals, and dioxins. The type and quantity of particles and chemicals in smoke differs depending upon what is burning, just how much oxygen is readily available, and the burn temperature level.
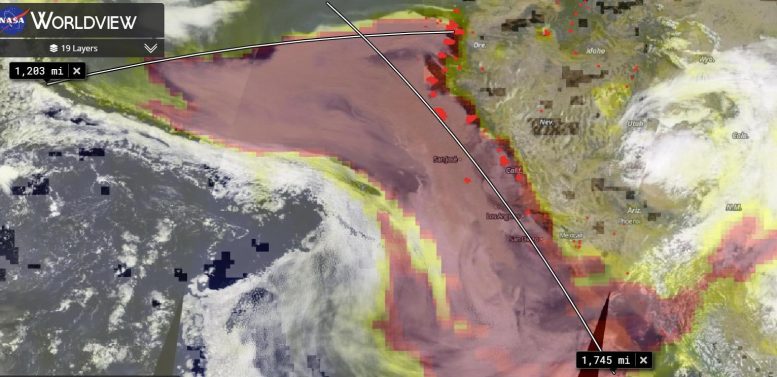
This image determines the ranges that the smoke has actually taken a trip both east-west and north-south. Measurement was achieved utilizing the measurement tool discovered within NASA’s Worldview application.
Credit: NASA Worldview
Exposure to high levels of smoke as evidenced in these wildfires must be prevented. Individuals are encouraged to restrict their physical effort if direct exposure to high levels of smoke cannot be prevented. Individuals with cardiovascular or breathing conditions (e.g., asthma), fetuses, babies, kids, and the senior might be more susceptible to the health impacts of smoke direct exposure.
Residents of these locations are on notification that sundowns will be much redder and more orange for a while. The factor? The size of the smoke particles is ideal for removing other colors suggesting that red, pink and orange colors can be seen more clearly in the sky. More orange and red sundowns are most likely as long as the smoke remains.
NASA’s Earth Observing System Data and Information System (EOSDIS) Worldview application supplies the ability to interactively search over 700 worldwide, full-resolution satellite images layers and after that download the underlying information. Many of the readily available images layers are upgraded within 3 hours of observation, basically revealing the whole Earth as it looks “right now.” Actively burning fires, found by thermal bands, are revealed as red points. Image Courtesy: NASA Worldview, Earth Observing System Data and Information System (EOSDIS).





