Scientists are checking out hydrogen as a tidy energy source to fight environment modification, concentrating on its production through water electrolysis and usage in fuel cells for transport, lining up with the objective of net-zero carbon emissions by 2050.
What Is Hydrogen Energy?
As the impacts of environment modification take hold, our world deals with record heat waves, unmatched storms, historical dry spells, and wildfires. Scientists have actually connected these occasions to greenhouse gases like co2 in the environment, much of which is produced by human activity.
But what if, rather of launching damaging greenhouse gases into the environment, our planes and cars and trucks could work on fuel produced from water, utilizing electrical power from the sun or wind? What if this eco-friendly fuel could supply backup power to the electrical grid and be bought from sustaining stations throughout the country?
In this Science 101 video, researchers Debolina Dasgupta and Nancy Kariuki explain the science, innovation, and applications of hydrogen energy. Hydrogen is the most basic chemical aspect, or kind of < period class ="glossaryLink" aria-describedby ="tt" data-cmtooltip ="<div class=glossaryItemTitle>atom</div><div class=glossaryItemBody>An atom is the smallest component of an element. It is made up of protons and neutrons within the nucleus, and electrons circling the nucleus.</div>" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}] "tabindex =(************************************************* )function ="link" > atom, and an abundance of hydrogen exists within the water on our world.It is naturally restored by the water cycle, and when utilized as fuel, it launches no damaging emissions. For these factors, hydrogen might play a significant function in promoting a cleaner environment and minimizing greenhouse gas emissions in sectors varying from transport to the grid.Scientists at the U.S.Department ofEnergy’s(********************************************************************************************************************************************** )NationalLaboratory are leveraging first-rate centers and proficiency to decrease the expense of hydrogen production and establish budget-friendly fuel cells for hydrogen-powered automobiles.They’re likewise evaluating approaches of hydrogen production, transportation, storage and utilize to decrease greenhouse gas emissions.
Scientists are working to make this vision a truth utilizing the energy within hydrogen, which assures to play a significant function in promoting a cleaner environment and accomplishing the U.S. objective to obtain net-zero carbon emissions by2050– to put it simply, getting rid of carbon from the environment at the very same rate it is discharged.
Hydrogen is the most basic chemical aspect, or kind of atom.It includes simply one proton and one electron.(************************************************************************************************************************* )is likewise the most plentiful aspect, comprising around 75% of the recognized matter in deep space. Vast quantities of hydrogen exist in water and living things.

An abundance of hydrogen exists within the water on our world, and it is naturally restored by the water cycle. When utilized as fuel, it launches no carbon emissions, making it an appealing tidy energy source. Credit: Argonne National Laboratory
The hydrogen particle, including 2 hydrogen atoms, can be utilized to produce carbon-free energy. Hydrogen particles bring a great deal of energy; a pound of hydrogen includes practically 3 times the energy of a pound of gas or diesel.
However, hydrogen particles are not plentiful on Earth, comprising less than 0.0001% of our environment. Because of this, hydrogen should be produced from other compounds which contain it. The most typical method to produce hydrogen that does not utilize nonrenewable fuel sources is to divide water (H 2 O) into hydrogen (H 2) and oxygen (O 2) utilizing electrical power. This procedure, called water electrolysis, is an appealing choice for carbon-free hydrogen production considering that the electrical power can be sourced from nuclear or renewable resource, such as wind and solar. Scientists and engineers are working to enhance and decrease the expense of hydrogen produced by water electrolysis.
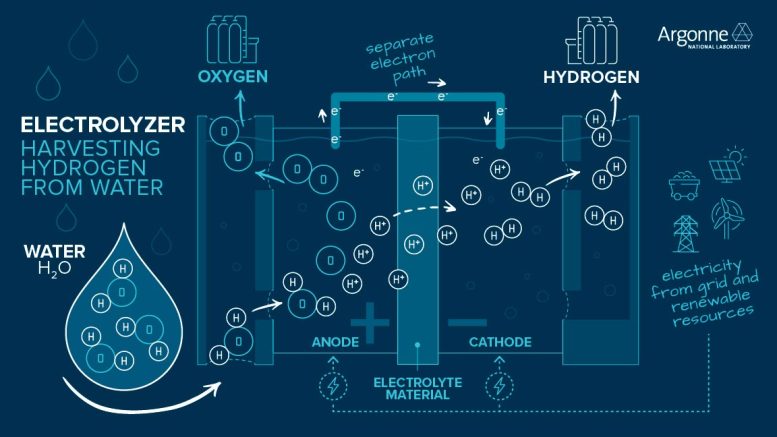
In electrolysis, water divides at the anode to form oxygen, hydrogen ions, and electrons. An electrolyte product permits hydrogen ions through, however forces electrons to stream independently to the cathode, where the 2 recombine to form hydrogen gas for usage as fuel. Credit: Argonne National Laboratory
They are likewise establishing approaches that transform solar power and water straight to hydrogen by utilizing and imitating biological procedures like < period class ="glossaryLink" aria-describedby ="tt" data-cmtooltip ="<div class=glossaryItemTitle>photosynthesis</div><div class=glossaryItemBody>Photosynthesis is how plants and some microorganisms use sunlight to synthesize carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water.</div>" data-gt-translate-attributes ="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex ="0" function ="link" > photosynthesis
There are a number of methods to utilize hydrogen for energy once it is produced.The most popular remains in fuel cells, which transform the chemical energy saved in hydrogen and oxygen into electrical power.Unlike with gasoline-fueled engines, there are no damaging emissions like co2.And unlike with batteries, fuel cell systems do not need prolonged downtimes for charging. They are refueled like gasoline-fueled engines, however with hydrogen.
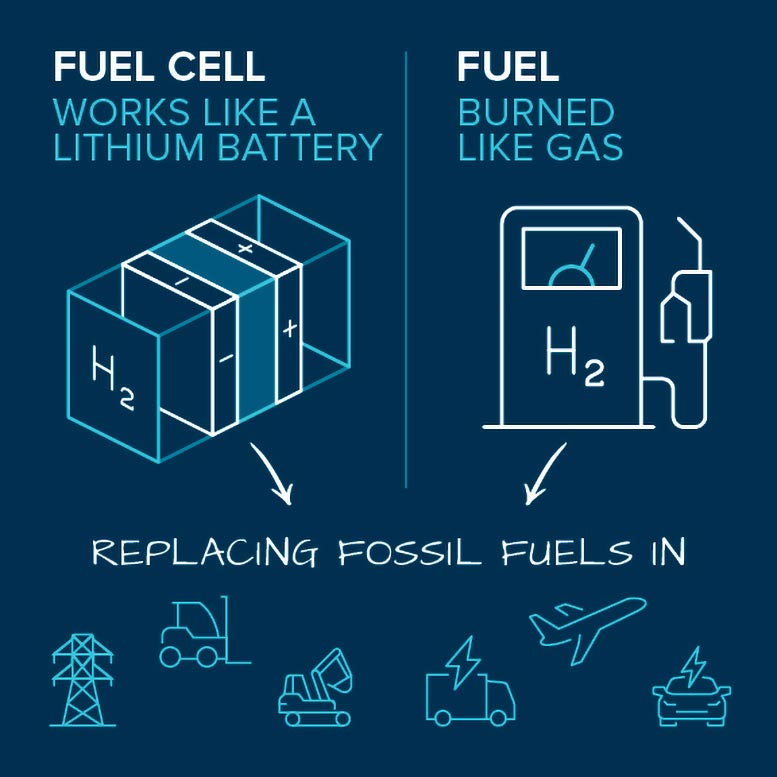
Hydrogen can be utilized in fuel cells or burned as fuel in engines. Scientists and engineers are working to enhance these innovations, which might change making use of nonrenewable fuel sources in transport and the grid. Credit: Argonne National Laboratory
A kind of hydrogen fuel cell being established for cars and trucks, trucks, forklifts, buses, ships, and trains divides hydrogen particles into electrons and protons. The electrons are required to stream through an electrical circuit, developing a supply of functional electrical power. Meanwhile, the protons have the ability to travel through a membrane, eventually recombining with the electrons and responding with oxygen particles from the air to produce water, the only emission.
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory are leveraging first-rate centers and proficiency to advance hydrogen science and innovation. Our scientists are reducing the expense of hydrogen production, establishing budget-friendly fuel cells for hydrogen-powered automobiles. They’re likewise evaluating approaches of hydrogen production, transportation, usage, and storage to decrease greenhouse gas emissions.





