Quantum mechanics, a field of physics checking out the basic nature of matter and energy, exposes phenomena like things existing in numerous states or locations, important for advancing contemporary innovations and safe interactions. Credit: SciTechDaily.com
What Is Quantum Mechanics?
Imagine a world where things can appear to exist in 2 locations simultaneously or impact each other from throughout deep space.
Although we do not see these kinds of things in our daily lives, comparable interests appear to exist all around us in the basic habits of our universe and its tiniest foundation. These strange qualities of nature are explained by a branch of physics called quantum mechanics.
In this Science 101: What is Quantum Mechanics video, Katherine Harmon– Argonne Scholar in the Materials Science Division– discusses what quantum mechanics is. Quantum mechanics is a theory that handles the most basic littles matter, energy and light and the methods they communicate with each other to comprise the world. This landmark theory came from the early 20 th century and is discovering lots of real-world applications in the 21 st century. Applying quantum mechanics in the lab, Argonne researchers like Harmon and lots of others are establishing innovations that might one day change society and our understanding of deep space. Quantum sensing units might identify formerly undetected cancer cells. A quantum web might guarantee unhackable interaction of messages and information. Quantum computer systems might resolve intricate issues classical computer systems can not. Quantum theory will likewise continue to advance our understanding of deep space from the detailed characteristics deep within an < period class =(******************************************* )aria-describedby ="tt" data-cmtooltip ="<div class=glossaryItemTitle>atom</div><div class=glossaryItemBody>An atom is the smallest component of an element. It is made up of protons and neutrons within the nucleus, and electrons circling the nucleus.</div>" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex ="0" function ="link" > atom to cosmic occasions as grand as the birth of deep space.(************ )
In the early1900 s, researchers started to establish quantum mechanics in order to describe the outcomes of a variety of experiments that defied any other analysis.Today, researchers utilize this theory to produce effective innovations– unhackable interaction of messages, faster drug discovery and higher-quality images on your phone and television screens.
So, what is quantum?In a more basic sense, the word“quantum” can describe the tiniest possible quantity of something.The field of quantum mechanics handles the most basic littles matter, energy and light and the methods they communicate with each other to comprise the world.
Unlike the method which we normally think of the world, where we envision things to have particle -or wave-like homes individually (baseballs and ocean waves, for instance), such concepts do not operate in quantum mechanics. Depending on the scenario, researchers might observe the very same quantum item as being particle-like or wave-like. For example, light can not be considered just a < period class ="glossaryLink" aria-describedby ="tt" data-cmtooltip ="<div class=glossaryItemTitle>photon</div><div class=glossaryItemBody>A photon is a particle of light. It is the basic unit of light and other electromagnetic radiation, and is responsible for the electromagnetic force, one of the four fundamental forces of nature. Photons have no mass, but they do have energy and momentum. They travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, and can have different wavelengths, which correspond to different colors of light. Photons can also have different energies, which correspond to different frequencies of light.</div>" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex ="0" function =(************************************************ )> photon (a light particle )or just a light wave, due to the fact that we may observe both sorts of habits in various experiments.
Day to day, we see things in one“state” at a time: here or there, moving or still, right-side up or upside down.(************************************************************************************* )state of an item in quantum mechanics isn’t constantly so simple.For example, before we seek to figure out the places of a set of quantum things, they can exist in what’s called a superposition– or an unique kind of mix– of several places.(************************************************************************************* )various possible states integrate and hinder each other like waves in a pond, and the things just have a guaranteed position after we have actually looked.(************************************************************************************** )is among the highlights that make quantum computer systems possible due to the fact that it allows us to represent details in brand-new and helpful methods.
Another fascinating quantum habits is tunneling, where a quantum item, like an electron, can often travel through barriers it otherwise would not have the ability to make it through. This occurs due to the fact that superposition permits a little possibility of the electron being on the opposite of the barrier. Quantum tunneling has applications such as in flash memory gadgets, effective microscopic lens and quantum computer systems.
When quantum things communicate, they are connected to each other through a connection called entanglement. This connection holds even if the things are separated by big ranges. Einstein called it“spooky action at a distance.” Scientists are using it for ultra-secure interaction, and it is an important function in < period class ="glossaryLink" aria-describedby ="tt" data-cmtooltip ="<div class=glossaryItemTitle>quantum computing</div><div class=glossaryItemBody>Performing computation using quantum-mechanical phenomena such as superposition and entanglement.</div>" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex ="0" function ="link" > quantum computing
At the U.S.Department ofEnergy’s( DOE)(*********************************************************************************************************************** )NationalLaboratory, researchers benefit from first-rate proficiency and research study centers to establish quantum innovations to shop, transportation and safeguard details, and to examine our universe, from the detailed characteristics deep within an atom to occasions as grand as the birth of deep space itself.Argonne likewise leads Q-NEXT, a DOE nationwide quantum details science proving ground working to establish quantum products and gadgets and catch the power of quantum innovation for interaction.
Credit:ArgonneNationalLaboratory
WhatIsQuantumInformationScience?
Leveraging counter-intuitive habits on the atomic scale to produce effective modifications in details science on a useful scale.
Scientists are racing to establish quantum-based systems that can keep, transportation, control, and safeguard details.
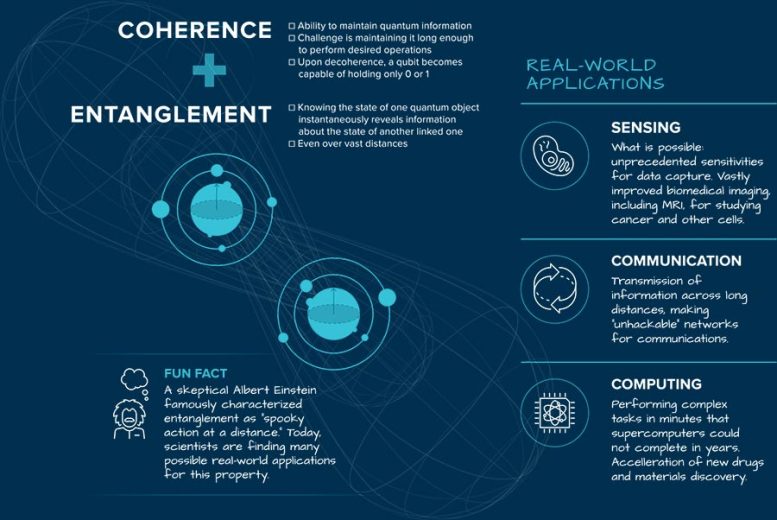
(**************** )Qubits– quantum bits– are the basic elements of quantum computing and other quantum details systems.They are comparable to the bit in classical computer systems, either 0 or 1.What makes qubits really unusual is that they can all at once be both 0 and 1.This overlapping state provides quantum computer systems enormously increased horse power.The qubit itself can can be found in various types– electrons, particles of light, even small problems in otherwise extremely structured products.
Scientists are looking for to develop qubits that preserve details in their quantum states for seconds(“coherence”) and can relate to other qubits(“entanglement”).
(**************** )Quantum innovations might change nationwide and monetary security, drug discovery, and the style and production of brand-new products, while deepening our understanding of deep space. (************ )(************* )
.





