Researchers at POSTECH have actually established a xanthan gum-based protective movie for battery electrodes, improving the resilience and effectiveness of zinc-ion batteries. This development marks a substantial action towards sustainable green energy services and addresses crucial obstacles in energy storage innovation.
Xanthan gum, a compound initially gotten from plants such as cabbage and acknowledged for its carb structure, is frequently utilized in cosmetics as a natural barrier to keep their skin advantages. In an ingenious improvement, xanthan gum has actually now been utilized to develop a protective guard for battery electrodes, instead of for the skin.
Professor Changshin Jo from the Graduate Institute of Ferrous & & Eco Materials Technology and the Department of Chemical Engineering and Jooyoung Jang, a PhD prospect, from the Department of Chemical Engineering at Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH), have actually crafted a protective movie by mixing polymers. This movie improves the resilience of battery electrodes, and their research study findings have actually been included in the global journal Energy Storage Materials
The Growing Importance of Energy Storage Systems
With renewable resource sources like solar energy being naturally periodic, the significance of energy storage systems (ESS) is gradually growing. ESS innovation allows the capture and effective usage of electrical power when required, making it an essential aspect in utilizing renewable resource. While lithium-ion (Li- ion) batteries have actually typically been used for ESS applications, their high expense and issues about lithium exhaustion have actually triggered continuous research study into alternative services.
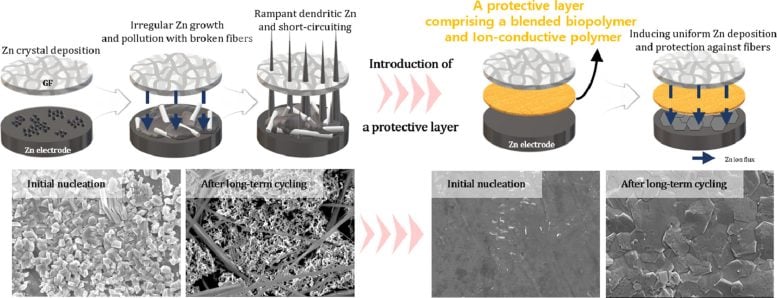
Introducing a xanthan gum-based guard to drive consistent zinc deposition. Credit: POSTECH
One appealing option to lithium is zinc (Zn), a plentiful aspect onEarth Zinc- ion batteries have the capability to keep substantial quantities of energy and are much safer in regards to fire threats compared to lithium-ion batteries. Nonetheless, accomplishing a constant deposition of zinc on the electrodes in ESS batteries is a difficult job, and the duplicated charging and releasing cycles tend to cause the development of twig-like crystals on the zinc surface area, lowering the battery’s durability.
Breakthrough in Battery Technology Using Xanthan Gum
In this examination, the research study group used the biopolymer xanthan gum in mix with an ionically conductive polymer to style a protective movie for the battery electrode. The interaction in between these 2 polymers yielded a smooth protective layer on the electrode’s surface area, efficiently protecting it from physical effects and chemical pollutants.
Furthermore, this protective movie was abundant in oxygen practical groups, which played an essential function in helping with the consistent nucleation of zinc, leading to the effective deposition of zinc on the electrode surface area. Consequently, the development of twig-like crystals on the zinc surface area was substantially alleviated, and the movie showed amazing stability even after withstanding 200 days of duplicated charging and releasing.
Professor Changshin Jo mentioned, “I hope this research will contribute to the advancement of ESS technology for sustainable green energy production.”
Reference: “Biopolymer-blended protective layer for use in stabilizing the zinc anode in metal battery applications” by Jooyoung Jang, Jinyoung Chun and Changshin Jo, 29 August 2023, Energy Storage Materials
DOI: 10.1016/ j.ensm.2023102948
The research study was sponsored by the National Research Foundation of Korea and the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning.





