After a number of weeks of bad weather condition and strong winds, the current set of high-altitude drop tests of the ExoMars parachutes happened in Kiruna, Sweden. The 15 m-wide very first phase primary parachute carried out perfectly at supersonic speeds, while the 35 m-wide 2nd phase parachute experienced one small damage, however decreased the mock-up of the landing platform as anticipated.
The ESA-Roscosmos ExoMars objective, with the Rosalind Franklin rover and Kazachok surface area platform, is set up for launch in September 2022. After a nine-month interplanetary cruise, a descent module including the rover and platform will be launched into the Martian environment at a speed of 21,000 km per hour.
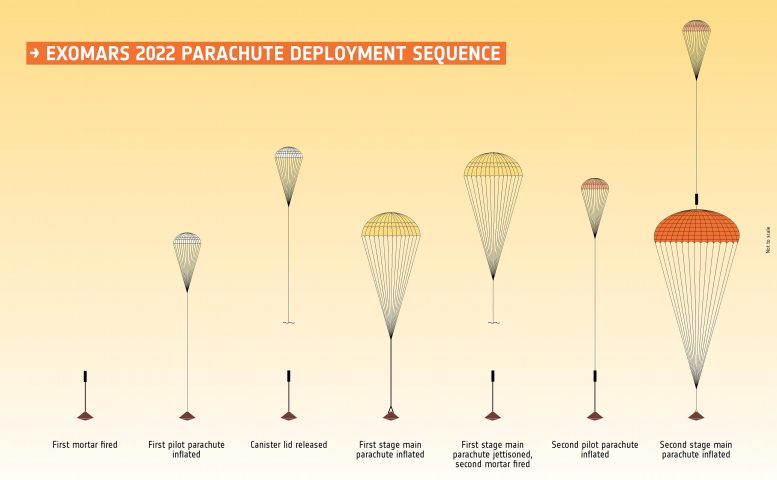
ExoMars 2022 parachute release series. The ExoMars parachute release series that will provide a surface area platform and rover to the surface area of Mars in 2023 (following launch in 2022). The graphic is not to scale, and the colors of the parachutes are for illustrative functions just.
The graphic highlights the centerpieces worrying the parachutes, a series that is started after substantial slowing down of the 3.8 m-wide entry module in the environment with the aeroshell’s heatshields. Then the very first pilot parachute is released, and soon after the very first primary phase parachute, which determines 15 m in size and has a disc-gap band style. It will open while the module is still taking a trip at supersonic speed and will be rejected prior to the release of the 2nd pilot chute and 2nd phase primary parachute as soon as at subsonic speeds. The 2nd phase primary parachute has a ring-slot style and is 35 m in size, the biggest to ever fly on Mars.
The 2nd pilot chute stays connected to the primary parachute in order to avoid rebound of the released parachute. During latter phases of the descent (not visualized) the aeroshell’s front heatshield will be disposed of, and the landing platform will be launched for its last descent and propulsive braking stage. Once securely on the surface area, it will consequently release ramps for the rover to drive down and on to Mars.
Credit: ESA
Slowing down needs a thermal guard, 2 primary parachutes – each with its own pilot chute for extraction – and a retro rocket propulsion system activated 20 seconds prior to goal. The 15m-wide very first phase primary parachute opens while the descent module is still taking a trip at supersonic speeds, and the 35 m-wide 2nd phase primary parachute is released at subsonic speeds.
Adjusting and evaluating the ExoMars parachutes has actually been a top priority following a series of not successful drop tests in 2019 and 2020. The group enhanced the style by running ground-based, quick turn-around vibrant extraction tests at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California in 2015. And to alleviate dangers prior to running these high-altitude drop tests, ESA purchased backup parachutes from the United States producer Airborne Systems, the extremely business that provided Perseverance’s parachute system.
The newest drop tests happened on 24 and 25 June at the Swedish Space Corporation Esrange center. Each high elevation drop test saw a dummy descent module lofted to an elevation of 29 km by a dizzying balloon pumped up with helium. Following release, the pilot chute extraction is started with a regulated extraction of the primary parachutes from their doughnut bags.
The very first test concentrated on verifying the Airborne Systems backup supersonic parachute – the very first drop test for this parachute in this ExoMars test project. The 2nd test was performed the following night utilizing the customized subsonic parachute and bag provided by the Italian business Arescosmo. Each test was developed to use the complete load anticipated throughout the Mars entry, descent, and landing, all with extra security margins.

ExoMars parachute effective healing. Credit: Vorticity
“We’re very happy to report that the first main parachute performed perfectly: we have a supersonic parachute design that can fly to Mars,” states Thierry Blancquaert, ExoMars program group leader, keeping in mind that “there will be at least two further opportunities to test this parachute design to gain further confidence”.
“The performance of the second main parachute was not perfect but much improved thanks to the adjustments made to the bag and canopy. After a smooth extraction from the bag, we experienced an unexpected detachment of the pilot chute during final inflation. This likely means that the main parachute canopy suffered extra pressure in certain parts. This created a tear that was contained by a Kevlar reinforcement ring. Despite that, it fulfilled its expected deceleration and the descent module was recovered in good state.”
The group will be searching in more information into the origin of this brand-new abnormality prior to settling the setup of the next set of drop tests predicted to occur in October/November 2021 from Oregon, U.S.A.. Earlier problems due to the friction in between canopy and bag now appear to be dealt with.
Any changes made to the parachute system will initially be checked on the vibrant extraction test rig at NASA/JPL to inspect how the release of the bag takes place, as it would take place in the martian environment. These tests can be duplicated on a fast turn-around and lower the danger of abnormalities.
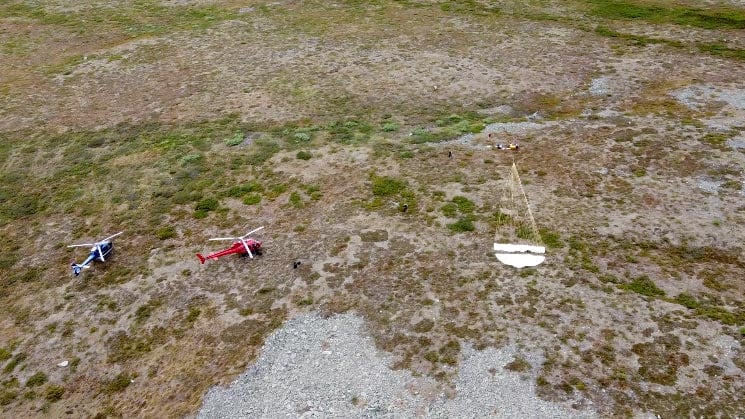

Recovery throughout the ExoMars parachute high-elevation drop tests in Kiruna. Credit: Vorticity
High-altitude drop tests need intricate logistics and stringent climate condition, making them hard to schedule, and are typically aborted at the last minute if the scenario modifications. The wind speed and instructions at numerous elevations needs to be thought about for a smooth climb of the balloon and the on-ground healing of the hardware considered that the drop zone can just be accessed through helicopter.
The system under test is developed to provide some telemetry in genuine time to a ground control centre to examine the deceleration profile. However, the real result of the test needs recuperating the parachutes, bags, hard drives and high-resolution video cameras.
“We were in the starting blocks twenty-four hours a day, seven days a week, waiting for a suitable test window to open for a month,” includes Thierry. “We’re relieved to have finally conducted these tests and extend our thanks to all of the ground teams who worked so hard amid the added COVID-related constraints to carry out the tests, as well as retrieve and inspect the parachutes.”
The analysis of the telemetry information will assist associate the primary parachutes release and the inflation designs. The group will now work to comprehend the 2nd pilot chute detachment, and to propose procedures that can solve this issue prior to the next high-altitude drop tests.
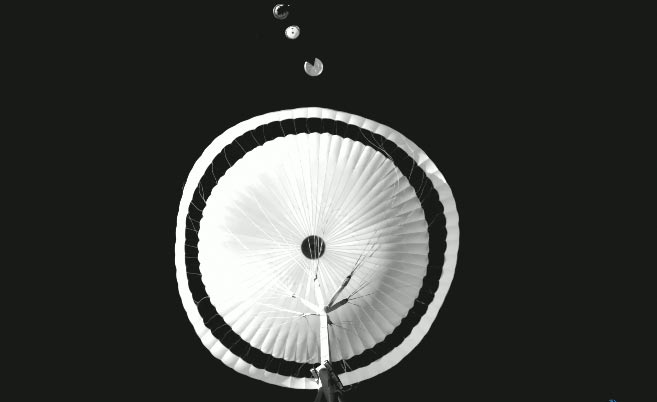

A best release for ExoMars. Credit: Vorticity
All parachute system certification activities are handled and carried out by a joint group including the ESA job (supported by the Directorate of Technology, Engineering and Quality), Thales Alenia Space Italy (ExoMars prime specialist, in Turin), Thales Alenia Space France (parachute system lead, in Cannes), Vorticity in the UK (Parachute style and test analysis, in Oxford) and Arescosmo in Italy (parachute and bags production, in Aprilia). NASA/JPL-Caltech has actually offered engineering consultancy, access to the vibrant extraction test center, and on-site assistance throughout these tests. The extraction tests are supported through an engineering assistance agreement with Airborne Systems, who likewise offered NASA’s Mars 2020 parachutes, and by Free Flight Enterprises for the arrangement of parachute folding and packaging centers. Airborne Systems is likewise supplying parachute style and production services because 2021.
Near Space Corporation offer the balloon launch services in Oregon. The Swedish Space Corporation Esrange center offers the balloon launch services in Kiruna.
The ExoMars objective will release on a Proton-M rocket with a Breeze-M upper phase from Baikonur, Kazakhstan, in the 20 September – 1 October 2022 launch window. Once landed securely in the Oxia Planum area of Mars on 10 June 2023, the rover will repel the surface area platform, looking for geologically fascinating websites to drill listed below the surface area, to identify if life ever existed on our next-door neighbor world. The ExoMars program, a joint venture in between ESA and Roscosmos, likewise consists of the Trace Gas Orbiter, which has actually been orbiting Mars because 2016. As well as its own science objective, Trace Gas Orbiter will offer important information relay services for the surface area objective; it is currently supplying information relay assistance for NASA’s surface area objectives, consisting of the arrival of the Mars 2020 Perseverance rover in February 2021.





