HKUST’s Vice-President (Research and Development)Prof Nancy IP (Middle) and her research study staff member– consisting of doctoral traineeMr Jason JIANG Yuanbing (2nd left) who is the very first author of this term paper. Credit: HKUST
An global research study group led by HKUST has actually established a basic however robust blood test from Chinese client information for early detection and screening of Alzheimer’s illness (ADVERTISEMENT) for the very first time, with an precision level of over 96%.
Currently, medical professionals primarily depend on cognitive tests to identify an individual with ADVERTISEMENT. Besides medical evaluation, brain imaging and lumbar leak are the 2 most frequently utilized medical treatments to find modifications in the brain brought on by ADVERTISEMENT. However, these approaches are pricey, intrusive, and regularly not available in lots of nations.
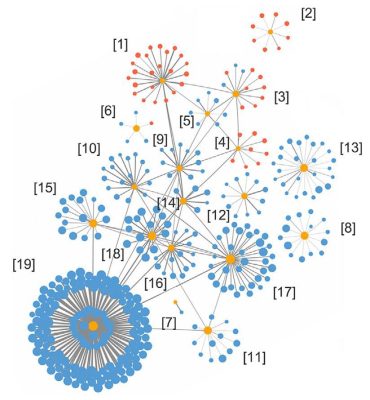
The research study group determined 19 plasma center proteins (suggested as yellow dots in the figure) in ADVERTISEMENT clients, which are irregular compared to healthy individuals. Credit: HKUST
Now, a group led byProf Nancy IP, Vice-President for Research and Development at HKUST, has actually determined 19 out of the 429 plasma proteins related to ADVERTISEMENT to form a biomarker panel agent of an “AD signature” in the blood. Based on this panel, the group has actually established a scoring system that identifies ADVERTISEMENT clients from healthy individuals with more than 96% precision. This system can likewise separate amongst the early, intermediate, and late phases of ADVERTISEMENT, and can be utilized to keep an eye on the development of the illness in time. These amazing findings have actually resulted in the advancement of a high-performance, blood-based test for ADVERTISEMENT, and might likewise lead the way to unique restorative treatments for the illness.
“With the advancement of ultrasensitive blood-based protein detection technology, we have developed a simple, noninvasive, and accurate diagnostic solution for AD, which will greatly facilitate population-scale screening and staging of the disease,” statedProf Nancy Ip, Morningside Professor of Life Science and the Director of the State Key Laboratory of Molecular Neuroscience at HKUST.
The work was carried out in cooperation with scientists at University College London and clinicians in regional medical facilities consisting of the Prince of Wales Hospital and Queen ElizabethHospital The discovery was used the distance extension assay (PEA)– an advanced ultrasensitive and high-throughput protein measurement innovation, to analyze the levels of over 1,000 proteins in the plasma of ADVERTISEMENT clients in Hong Kong.

Using the blue gadget (envisioned) that carries out the ultrasensitive distance extension assay innovation,Prof Ip and her group established a blood test for early detection and screening of Alzheimer’s illness from Chinese client information, with a precision level of over 96%. Credit: HKUST
As the most extensive research study of blood proteins in ADVERTISEMENT clients to date, the work has actually just recently been released in Alzheimer’s & & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association, and has actually likewise been included and actively gone over on various academic exchange platforms on ADVERTISEMENT research study such as Alzforum.
ADVERTISEMENT, which impacts over 50 million individuals worldwide, includes the dysfunction and loss of brain cells. Its signs consist of progressive amnesia along with impaired motion, thinking, and judgment. While clients typically just look for medical attention and are identified when they have memory issues, ADVERTISEMENT impacts the brain a minimum of 10-20 years prior to signs appear.
Reference: “Large-scale plasma proteomic profiling identifies a high-performance biomarker panel for Alzheimer’s disease screening and staging” by Yuanbing Jiang, Xiaopu Zhou, Fanny C. Ip, Philip Chan, Yu Chen, Nicole C.H. Lai, Kit Cheung, Ronnie M.N. Lo, Estella P.S. Tong, Bonnie W.Y. Wong, Andrew L.T. Chan, Vincent C.T. Mok, Timothy C.Y. Kwok, Kin Y. Mok, John Hardy, Henrik Zetterberg, Amy K.Y. Fu and Nancy Y. Ip, 25 May 2021,.
DOI: 10.1002/ alz.12369





