Researchers propose a reevaluation of the cultural advancement of Homo sapiens throughout their dispersal throughout Eurasia, recommending a steady and complicated procedure instead of a quick transformation. Their research study challenges conventional views by concentrating on the advancement of stone tool innovation, showing that considerable developments took place after the preliminary dispersal of Homo sapiens, especially with the advancement of bladelet innovation. Credit: SciTechDaily.com
Contrary to previous beliefs, considerable improvements in stone tool innovation emerged after, not previously, Homo sapiens spread throughout Eurasia, marking an intricate evolutionary journey.
A research study led by scientists at the < period class ="glossaryLink" aria-describedby ="tt" data-cmtooltip ="<div class=glossaryItemTitle>Nagoya University</div><div class=glossaryItemBody>Nagoya University, sometimes abbreviated as NU, is a Japanese national research university located in Chikusa-ku, Nagoya. It was the seventh Imperial University in Japan, one of the first five Designated National University and selected as a Top Type university of Top Global University Project by the Japanese government. It is one of the highest ranked higher education institutions in Japan.</div>" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex ="0" function ="link" >NagoyaUniversityMuseum in Japan might alter how we comprehend the cultural advancement ofHomo sapiens at the time of their dispersal throughoutEurasia about50,000 to40, 000 years back.These findings challenge conventional beliefs about the timing and nature of cultural shifts throughout this vital duration in human history.
Published in < period class ="glossaryLink" aria-describedby ="tt" data-cmtooltip ="<div class=glossaryItemTitle>Nature Communications</div><div class=glossaryItemBody><em>Nature Communications</em> is a peer-reviewed, open-access, multidisciplinary, scientific journal published by Nature Portfolio. It covers the natural sciences, including physics, biology, chemistry, medicine, and earth sciences. It began publishing in 2010 and has editorial offices in London, Berlin, New York City, and Shanghai. </div>" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex ="0" function ="link" >Nature(****************************************************************************************************************************************************************** ), the scientists’ insights into stone tool innovation recommend that the typically held view of a‘revolution’ in culture and innovation that enabled anatomically contemporary people to outcompeteNeanderthals and other antiquated people was a more nuanced and complex procedure of cultural advancement.
The group of scientists concentrated on theMiddle-Upper(***************************************************************************************************************************** )( MP-UP )cultural shift, a crucial limit in between 2 essential stages in our advancement:
- TheMiddlePaleolithic duration(250,000 to40,000 years ago) saw anatomically contemporary people existing together with Neanderthals and antiquated people existing at the exact same time. Culturally, anatomically contemporary people and Neanderthals had comparable stone tool innovation, such as making tools utilizing ‘Levallois methods’, which included striking stones with a hammer-like tool.
- The Upper Paleolithic duration (50,000 and 12,000 years ago) is the duration in which anatomically contemporary people made broad geographical growths, and antiquated people went extinct. During this duration, brand-new cultural components emerged in different worlds, consisting of tool innovation, food acquisition, seafaring, and creative expression in accessories and cavern art.
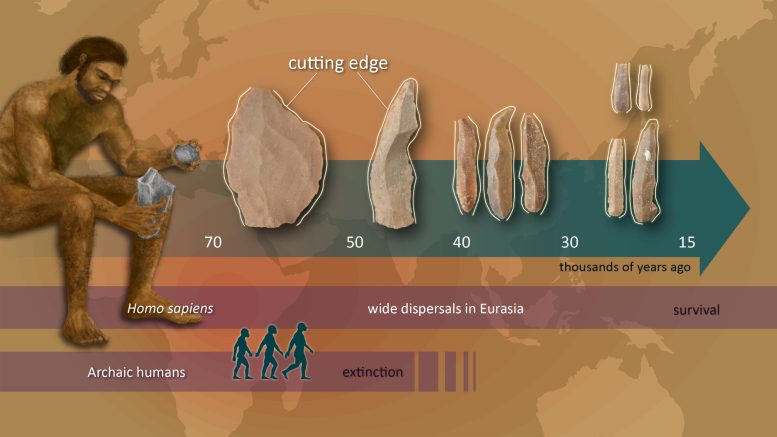
The boost in the efficiency of stone tool cutting-edge (displayed in white lines) did not happen before or at the start of Homo sapiens’ broad dispersals in Eurasia however consequently took place after their preliminary dispersals, accompanying the advancement of bladelet innovation in the Early UpperPaleolithic Credit: Reiko Matsushita
Traditionally, scholars saw the MP-UP shift as an abrupt modification marked by the innovative introduction of brand-new cultural components. An example is the assumed unexpected neural anomaly in Homo sapiens, which led to their exceptional cognitive capabilities. This modification enabled them to eventually outcompete other antiquated people and drive the Neanderthals to termination. However, this research study challenges this paradigm.
The scientists analyzed the efficiency of stone tools with a cutting edge over a 50,000- year period that included 6 cultural stages from the Late Middle Paleolithic, through the Upper Paleolithic, to the Epipaleolithic duration. They found that the significant boost in ingenious efficiency did not happen before or at the start of the extensive dispersal of Homo sapiens inEurasia Rather, it consequently took place after their preliminary dispersals, accompanying the advancement of bladelet innovation in the Early Upper Paleolithic.
This result reveals a complex procedure of cultural modification including several phases instead of a single ‘revolution.’
According to the lead scientist Professor Seiji Kadowaki, the cultural shift from the Middle to the Upper Paleolithic was a complex, evolutionary procedure including several elements and modifications happening over a prolonged duration. He stated, “In terms of cutting-edge productivity, Homo sapiens did not start to spread to Eurasia after a quick revolution in stone tool technology, but rather the innovation in the ‘cutting-edge’ productivity occurred later, in tandem with the miniaturization of stone tools like bladelets.”
Reference: 7 February 2024, Nature Communications
DOI: 10.1038/ s41467-024-44798- y





