The Advanced Photon Source (APS) at Argonne National Laboratory is an important center for clinical research study, offering an effective X-ray light to study products in information. By using a better take a look at internal procedures, such as in batteries, APS help in technological developments. With its considerable upgrade, the APS will increase its brightness and research study ability, continuing to add to international health, security, and clinical development. Credit: SciTechDaily.com
What Is an X-Ray Light Source?
To establish treatments to fight lethal contagious illness, we require to comprehend the organisms that trigger them. To style the next generation of electrical automobiles, we require to develop much better, longer-lasting batteries to power them. To develop more effective, more secure plane engines, we require more powerful, more resilient products that will not break under tension.
In this Science 101: What is X-ray Light video, researchers Jessica McChesney and Gilberto Fabbris discuss what X-ray light is, and how they utilize it at Argonne’s Advanced Photon Source (APS). X-ray light is high-energy light that exists on the electro-magnetic spectrum. This spectrum consists of the series of all electro-magnetic waves, from the longest waves with the most affordable energy (AM radio), to those in the middle (noticeable light), to the quickest waves with the greatest energy (gamma rays). The APS at Argonne utilizes X-rays, which are on completion of the spectrum that has much shorter wavelengths. The much shorter wavelengths permit the X-rays to go through numerous compounds, which permits researchers like Jessica and Gilberto to peer deep into things and find brand-new understanding about the structure and function of products. The APS is among the most effective X-ray lights on the planet, and more than 5,500 researchers from worldwide usage this substantial research study center each year to check brand-new products, develop much better batteries, and discover services for the greatest issues dealing with humankind.
To do all of those things, and more, an effective X-ray light is required. X-rays are light, however they are not the noticeable light one usually thinks about when you hear the word. You might recognize with the X-ray devices dental professionals utilize to take photos of the within teeth. A light such as the Advanced Photon Source (APS), a U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) Office of Science User Facility situated at DOE’s Argonne National Laboratory, produces comparable X-ray light, however a billion times brighter.
What can be finished with a light that brilliant? The APS works like a huge microscopic lense, however unlike noticeable light, X-rays are permeating, making it possible for researchers to see deep inside products. The X-ray beams can be focused so firmly that researchers can utilize them to“see” what occurs inside a battery throughout usage, for instance, so more energy-efficient variations can be established.
The APS, and other lights worldwide, have actually been enhancing our lives for years. The innovation that powers them– particle velocity– has actually been around because the 1920 s.
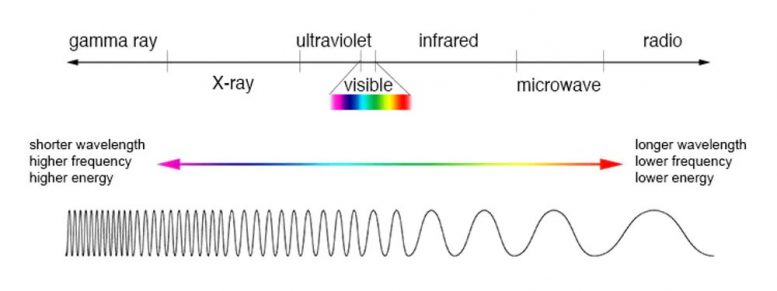
The electro-magnetic spectrum is the series of all kinds of EM radiation– energy that takes a trip and expands as it goes. The sun is much hotter than the Earth, so it discharges radiation at a greater energy level, which has a much shorter wavelength. Credit: NASA
At the heart of the APS is a storage ring, about two-thirds of a mile around. It’s so big you might fit a baseball arena inside it. Its task is to flow particles called electrons with high accuracy and at a constant speed really close to the speed of light. Electrons travel around this ring numerous billions of times a day, launching brilliant light at each bend in the track. The APS sends out that light to experiment stations situated all around the ring, where various kinds of science experiments are carried out.
The APS is a nationwide user center, indicating this resource is provided to researchers worldwide. There is no charge for researchers to utilize it, offered that their information is launched openly. More than 5,500 researchers from worldwide utilize the APS yearly to study a wide range of things, from brand-new methods to fight greenhouse gases to brand-new approaches of strengthening our roadways and bridges.
The APS has actually been a world-leading X-ray light because it was very first integrated in the 1990 s, and its future will get a lot better. An enormous upgrade is changing the existing storage ring with one that will create X-rays as much as 500 times brighter than those produced today, making it possible for more experiments and developments that will enhance our lives. Along with other lights worldwide, the APS will continue to make it possible for researchers to keep us much healthier, keep us more secure, and enhance our understanding of the world around us.
Credit: Argonne National Laboratory
How Does an X-Ray Light Source Work?
The Advanced Photon Source develops ultrabright X-ray beams to light the method towards brand-new discoveries.
An effective light such as the Advanced Photon Source (APS) resembles the X-ray devices dental professionals utilize, other than the light it develops is a billion times brighter.
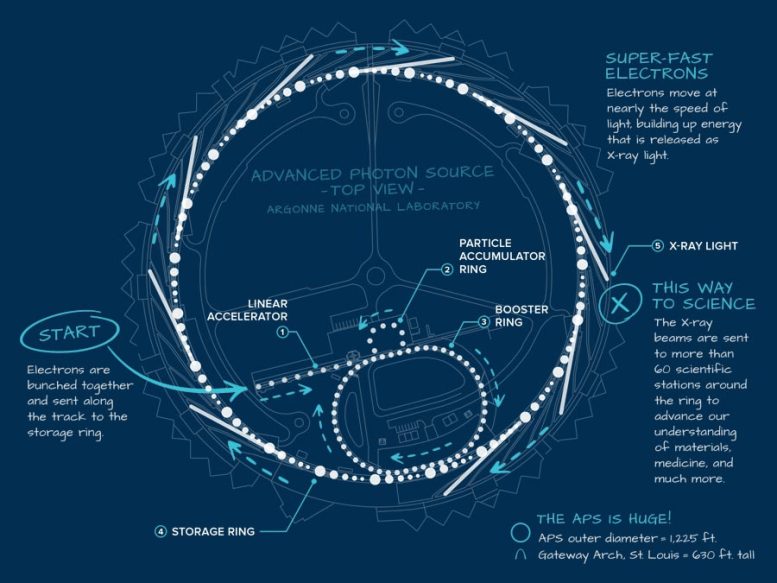
- The heart of the APS is a series of devices called accelerators that utilize magnets to move small particles called electrons. The electrons are bunched together and sent out relocating a straight line down a direct accelerator.
- The particle accumulator ring groups the lots more detailed together.
- The booster ring flows them as they develop speed and energy.
- The particles are then injected into the storage ring. Electrons travel around this ring billions of times a day. At each bend in the track, they launch light in the kind of < period class ="glossaryLink" aria-describedby ="tt" data-cmtooltip ="<div class=glossaryItemTitle>photon</div><div class=glossaryItemBody>A photon is a particle of light. It is the basic unit of light and other electromagnetic radiation, and is responsible for the electromagnetic force, one of the four fundamental forces of nature. Photons have no mass, but they do have energy and momentum. They travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, and can have different wavelengths, which correspond to different colors of light. Photons can also have different energies, which correspond to different frequencies of light.</div>" data-gt-translate-attributes ="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex ="0" function ="link" > photon particles.
- Those photons are the X-ray light that is sent out to clinical stations all around the ring.Scientists utilize that really brilliant light to see deep inside products.





