This illustration reveals the place of the C-19 excellent stream (orange, vertical stream of stars in lower left), which was just recently found at the edge of our Milky WayGalaxy Observations utilizing the Gemini North telescope– part of the global Gemini Observatory, a Program of NSF’s NOIRLab– expose that the stars in this stream were as soon as part of an ancient globular star cluster that was torn apart by gravitational interactions with our galaxy. The Large Magellanic Cloud and Small Magellanic Cloud (satellite galaxies of the Milky Way) appear in the lower right. Credit: International Gemini Observatory/ NOIRLab/NSF/AURA/ J. da Silva/Spaceengine, Acknowledgment: M. Zamani (NSF’s NOIRLab)
985% of the Sun is comprised of 2 light chemical components, hydrogen and helium, while the staying 1.5% includes other much heavier components such as carbon, oxygen, and iron. The abundance of these much heavier components in a star is called its ‘metallicity’, and differs from star to star. It now ends up that our Galaxy is house to an outstanding structure distinctively made from stars with incredibly low metallicity, with a heavy aspect material 2,500 times lower than that of theSun This is well listed below that of any other recognized excellent structure in the Universe.
This discovery, made by a worldwide group led by a CNRS scientist at the Strasbourg Astronomical Observatory (CNRS/ University of Strasbourg), and including researchers from the Galaxies, Stars, Physics and Instrumentation Laboratory (Paris Observatory– PSL/ CNRS) and at the J-L Lagrange Laboratory (CNRS/ Côte d’Azur Observatory), is released on January 5, 2022, in the journal Nature
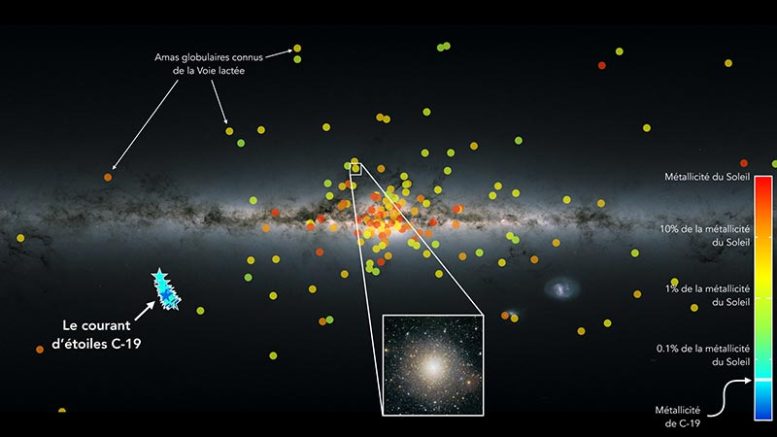
Credit: Distribution of extremely thick groups of stars in the Milky Way, called globular clusters, superimposed on a map of the Milky Way put together from information gotten with the Gaia SpaceObservatory Each dot represents a cluster of a couple of thousand to numerous million stars, as in the insert picture of the Messier 10 cluster. The colour of the dots reveals their metallicity, simply put, their abundance of heavy components relative to theSun The C-19 stars are suggested by the light blue signs. Credit: © N. Martin/ Strasbourg Astronomical Observatory/ CNRS; Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope/ Coelum; ESA/ Gaia/ DPAC
This group of stars all come from an outstanding structure in the Milky Way called C-19 Not just does this discovery obstacle our existing understanding and designs of the development of these excellent groupings, which omit the presence of structures made up just of such stars, it likewise opens a special and direct window onto the extremely earliest ages of star development and the advancement of excellent structures in the extremely remote past. Since heavy components were produced by succeeding generations of enormous stars, the extremely low metallicity of the C-19 stars reveals that they were formed just a brief time after the birth of the Universe.
For more on this discovery, see Ruins of Ancient Star Cluster Discovered at the Fringes of Our Galaxy.
Reference: “A stellar stream remnant of a globular cluster below the metallicity floor” by Nicolas F. Martin, Kim A. Venn, David S. Aguado, Else Starkenburg, Jonay I. Gonz ález Hern ández, Rodrigo A. Ibata, Piercarlo Bonifacio, Elisabetta Caffau, Federico Sestito, Anke Arentsen, Carlos Allende Prieto, Raymond G. Carlberg, Sébastien Fabbro, Morgan Fouesneau, Vanessa Hill, Pascale Jablonka, Georges Kordopatis, Carmela Lardo, Khyati Malhan, Lyudmila I. Mashonkina, Alan W. McConnachie, Julio F. Navarro, Rub én Sánchez-Janssen, Guillaume F. Thomas, Zhen Yuan and Alessio Mucciarelli, 5 January 2022, Nature
DOI: 10.1038/ s41586-021-04162 -2
This work was performed as part of the Pristine study, with ESA’s Gaia area observatory, the Canada-France-Hawaii Telescope (Hawaii), the Gemini North telescope (Hawaii) and the GTC telescope (Canary Islands).





