University of Cincinnati chemical engineering trainee Tianyu Zhang holds up a vial of graphene utilized as a driver to transform co2 into methane. Credit: Andrew Higley/ UC Creative
A filling station on Mars? Chemical engineers visualize the possibilities.
Engineers at the University of Cincinnati are establishing brand-new methods to transform greenhouse gases to sustain to resolve environment modification and get astronauts house from Mars.
UC College of Engineering and Applied Science assistant teacher Jingjie Wu and his trainees utilized a carbon driver in a reactor to transform co2 into methane. Known as the “Sabatier reaction” from the late French chemist Paul Sabatier, it’s a procedure the International Space Station utilizes to scrub the co2 from air the astronauts breathe and produce rocket fuel to keep the station in high orbit.
But Wu is believing much larger.
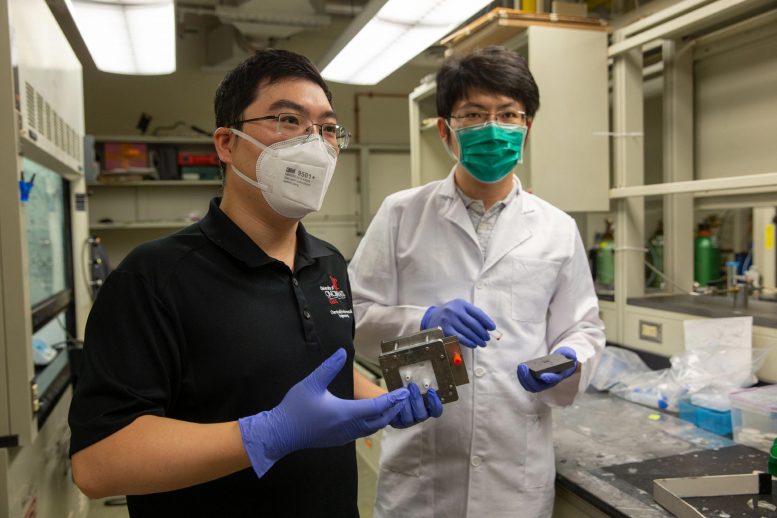

UC chemical engineering assistant teacher Jingjie Wu, left and doctoral trainee Tianyu Zhang are try out various drivers to transform co2 to storable fuel to resolve environment modification. Credit: Andrew Higley/ UC Creative
The Martian environment is made up nearly totally of co2. Astronauts might conserve half the fuel they require for a return journey house by making what they require on the red world once they show up, Wu stated.
“It’s like a gas station on Mars. You could easily pump carbon dioxide through this reactor and produce methane for a rocket,” Wu stated.
UC’s research study was released in the journal Nature Communications with partners from Rice University, Shanghai University, and East China University of Science and Technology.
Wu started his profession in chemical engineering by studying fuel cells for electrical lorries however started taking a look at co2 conversion in his chemical engineering laboratory about 10 years back.
UC chemical engineer Jingjie Wu holds up the reactor where a driver transforms co2 into methane. UC’s research study makes him positive that researchers will have the ability to get rid of co2 from the environment. Credit: Andrew Higley/ UC Creative + Brand
“I realized that greenhouse gases were going to be a big issue in society,” Wu stated. “A lot of countries realized that carbon dioxide is a big issue for the sustainable development of our society. That’s why I think we need to achieve carbon neutrality.”
The Biden Administration has actually set an objective of attaining a 50% decrease in greenhouse gas contaminants by 2030 and an economy that counts on renewable resource by 2050.
“That means we’ll have to recycle carbon dioxide,” Wu stated.
Wu and his trainees, consisting of lead author and UC doctoral prospect Tianyu Zhang, are try out various drivers such as graphene quantum dots– layers of carbon simply nanometers huge– that can increase the yield of methane.
“Right now we have excess green energy that we just throw away. We can store this excess renewable energy in chemicals.”
— Jingjie Wu, UC assistant teacher of chemical engineering
Wu stated the procedure holds pledge to assist alleviate environment modification. But it likewise has a huge business benefit in producing fuel as a by-product.
“The process is 100 times more productive than it was just 10 years ago. So you can imagine that progress will come faster and faster,” Wu stated. “In the next 10 years, we’ll have a lot of startup companies to commercialize this technique.”
Wu’s trainees are utilizing various drivers to produce not just methane however ethylene. Called the world’s crucial chemical, ethylene is utilized in the manufacture of plastics, rubber, artificial clothes, and other items.
“Green energy will be very important. In the future, it will represent a huge market. So I wanted to work on it,” Zhang stated.
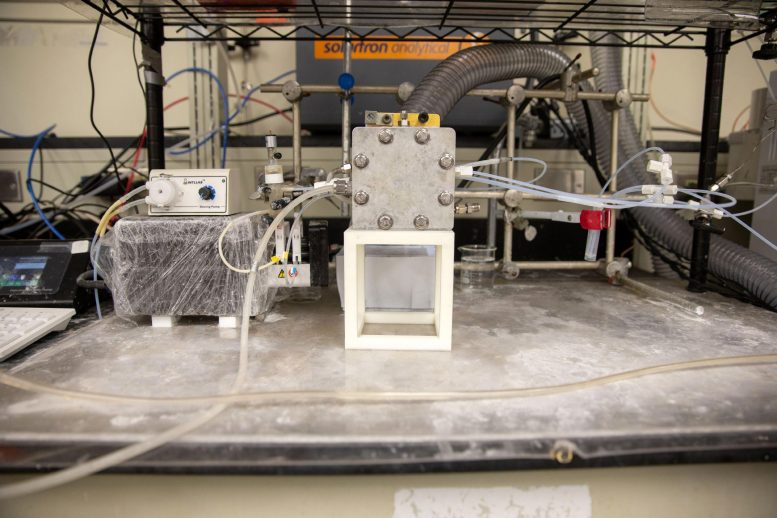
An speculative reactor utilizes graphene quantum dots as a driver to transform co2 into methane. Credit: Andrew Higley/ UC Creative
Synthesizing fuel from co2 ends up being much more commercially practical when paired with renewable resource such as solar or wind power, Wu stated.
“Right now we have excess green energy that we just throw away. We can store this excess renewable energy in chemicals,” he stated.
The procedure is scalable for usage in power plants that can produce lots of co2. And it’s effective considering that the conversion can occur right where excess co2 is produced.
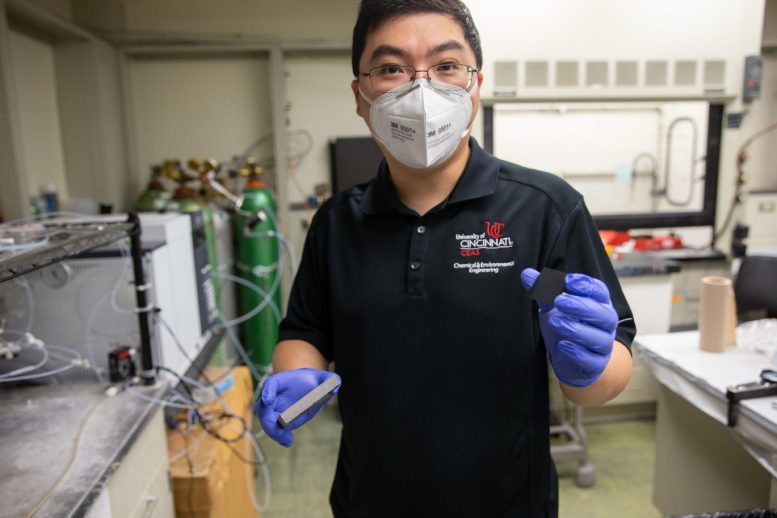

UC chemical engineer Jingjie Wu is try out various drivers to transform co2 to fuels such as methane to resolve environment modification. Credit: Andrew Higley/ UC Creative
Wu stated advances in fuel production from co2 make him more positive that human beings will set foot on Mars in his life time.
“Right now if you want to come back from Mars, you would need to bring twice as much fuel, which is very heavy,” he stated. “And in the future, you’ll need other fuels. So we can produce methanol from carbon dioxide and use them to produce other downstream materials. Then maybe one day we could live on Mars.”
Reference: “Regulation of practical groups on graphene quantum dots directs selective CO 2 to CH 4 conversion” by Tianyu Zhang, Weitao Li, Kai Huang, Huazhang Guo, Zhengyuan Li, Yanbo Fang, Ram Manohar Yadav, Vesselin Shanov, Pulickel M. Ajayan, Liang Wang, Cheng Lian and Jingjie Wu, 6 September 2021, Nature Communications
DOI: 10.1038/ s41467-021-25640 -1





