Deep inside the brain the putamen, not simply the cortex, adds to multitasking capability.
Multitasking efficiency originates from the speed of info exchange in between inner and external areas of the brain, according to brand-new research study in eNeuro.
Doing 2 things at the same time courts catastrophe, as multitasking needs external cortical brain areas to quickly interact with each other. The speed of this info exchange limitations multitasking ability yet can enhance with practice. But that’s not the entire story: multitasking likewise depends upon the striatum, a formerly ignored area deep inside the brain.
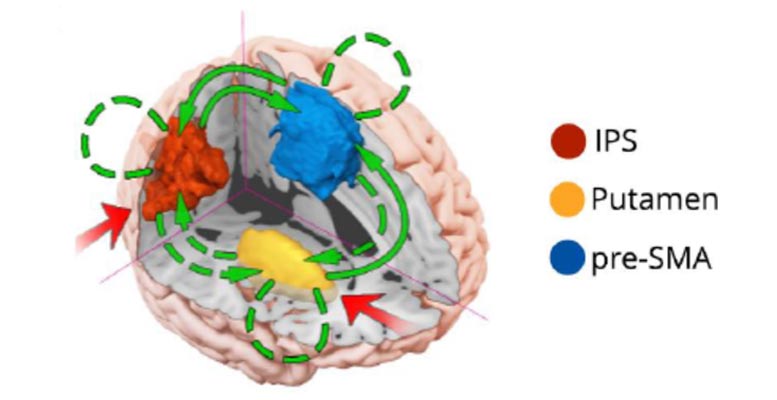
Proposed design for the modulatory impact of multitasking. Credit: Garner et al., eNeuro 2020
Garner et al. compared the brain activity of 100 healthy grownups prior to and after a week of multitasking practice. The individuals finished 2 various jobs, initially individually and after that at the exact same time. The putamen — a brain area in the striatum associated with regular habits — and 2 cortical areas were triggered by the jobs individually and increased activity throughout multitasking. After screening a range of possible designs, the research study group discovered that multitasking capability depended upon how successfully the putamen might exchange info with the cortical locations. A week of practice enhanced the individual’s job efficiency in show with a boost in interaction rates in between the putamen and the cortex.
Reference: “Cognitive Capacity Limits Are Remediated by Practice-Induced Plasticity Between the Putamen and Pre-Supplementary Motor Area” 17 August 2020, eNeuro.





