Graphic demonstrating how UV radiation on Earth has actually altered over the last 2.4 billion years. Credit: Gregory Cooke/ Royal Society Open Science
During long parts of the previous 2.4 billion years, the Earth might have been more unwelcoming to life than researchers formerly believed, according to brand-new computer system simulations.
Using a modern environment design, scientists now think the level of ultraviolet (UV) radiation reaching the Earth’s surface area might have been ignored, with UV levels depending on 10 times greater.
UV radiation is discharged by the sun and can harm and ruin biologically crucial particles such as proteins.
The last 2.4 billion years represents an essential chapter in the advancement of the biosphere. Oxygen levels increased from practically no to considerable quantities in the environment, with concentrations varying however ultimately reaching contemporary concentrations around 400 million years earlier.
During this time, more complicated multicellular organisms and animals started to colonize land.
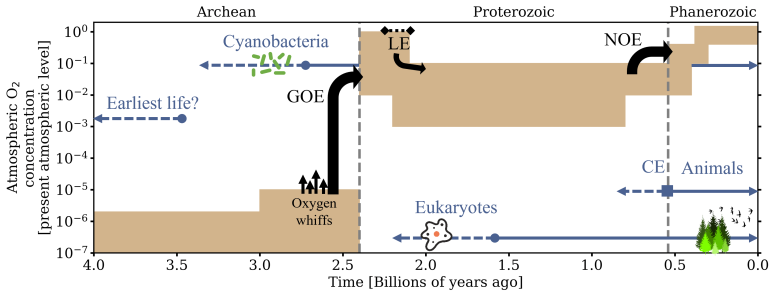
A rough overview of oxygen (O2) concentrations in Earth’s environment through time are shown in this figure. Brown obstructs reveal the approximated variety for O2 in regards to its present climatic level (which is 21% by volume). Grey- blue lines suggested numerous crucial occasions for the advancement of life, consisting of the development of eukaryotes and animals. Black arrows describe crucial occasions where climatic oxygen concentration altered. The Archean, Proterozoic, and Phanerozoic are geological eons. GOE = Great Oxidation Event; NOE = Neoproterozoic Oxidation Event; CE = Cambrian Explosion; LE = LomagundiExcursion Credit: Gregory Cooke/ Royal Society Open Science
Gregory Cooke, a PhD scientist at the University of Leeds who led the research study, stated the findings raise brand-new concerns about the evolutionary effect of UV radiation as numerous kinds of life are understood to be adversely impacted by extreme dosages of UV radiation.
He stated: “We understand that UV radiation can have dreadful impacts if life is exposed to excessive. For example, it can trigger skin cancer in human beings. Some organisms have reliable defense reaction, and numerous can fix a few of the damage UV radiation triggers.
“Whilst elevated amounts of UV radiation would not prevent life’s emergence or evolution, it could have acted as a selection pressure, with organisms better able to cope with greater amounts of UV radiation receiving an advantage.”
The research study “A revised lower estimate of ozone columns during Earth’s oxygenated history” was released on January 5, 2022, in the clinical journal Royal Society Open Science
The quantity of UV radiation reaching the Earth is restricted by the ozone in the environment, explained by the scientists as “…one of the most important molecules for life” since of its function in taking in UV radiation as it enters the Earth’s environment.
Ozone forms as an outcome of sunshine and chain reaction– and its concentration depends on the level of oxygen in the environment.
For the last 40 years, researchers have actually thought that the ozone layer had the ability to protect life from damaging UV radiation when the level of oxygen in the environment reached about one percent relative to today climatic level.
The brand-new modeling difficulties that presumption. It recommends the level of oxygen required might have been much greater, possibly 5% to 10% of present climatic levels.
As an outcome, there were durations when UV radiation levels at the Earth’s surface area were much higher, and this might have held true for the majority of the Earth’s history.
Mr Cooke stated: “If our modeling is a sign of climatic situations throughout Earth’s oxygenated history, then for over a billion years the Earth might have been bathed in UV radiation that was a lot more extreme than formerly thought.
“This may have had fascinating consequences for life’s evolution. It is not precisely known when animals emerged, or what conditions they encountered in the oceans or on land. However, depending on oxygen concentrations, animals and plants could have faced much harsher conditions than today’s world. We hope that the full evolutionary impact of our results can be explored in the future.”
The outcomes will likewise cause brand-new forecasts for exoplanet environments. Exoplanets are worlds that orbit other stars. The existence of specific gases, consisting of oxygen and ozone, might suggest the possibility of extra-terrestrial life, and the outcomes of this research study will assist in the clinical understanding of surface area conditions on other worlds.
Reference: “A revised lower estimate of ozone columns during Earth’s oxygenated history” by G. J. Cooke, D. R. Marsh, C. Walsh, B. Black and J.-F. Lamarque, 5 January 2022, Royal Society Open Science
DOI: 10.1098/ rsos.211165
The research study was moneyed by UK Science and Technology Facilities Council and included cooperation with researchers at the National Centre for Atmospheric Research, Rutgers University, and the City University of New York, all of which remain in the United States.





